


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 29-8-2016
Date: 7-8-2016
Date: 1-8-2016
|
Osmotic Pressure
Consider an ideal mixture of N0 monatomic molecules of type A and N2 monatomic molecules of type B in a volume V.
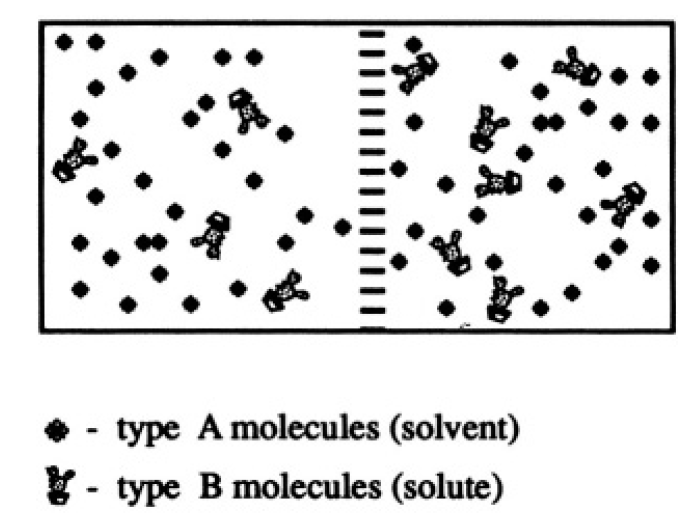
Figure 1.1
a) Calculate the free energy F(τ, V, N0, N1). Calculate the Gibbs potential G(τ, P, N0, N1). G is the Legendre transform of F with respect to V.
b) If N0 >> N1 the molecules of type A are called the solvent, and those of type B the solute. Consider two solutions with the same solvent (type A) and different concentrations of solute (type B molecules) separated by a partition through which solvent molecules can pass but solute molecules cannot (see Figure 1.1). There are N0 particles in volume V (or 2N0 in volume 2V), and N1 and N2 particles in volume V on the left and right of the membrane, respectively. Calculate the pressure difference across the membrane at a given temperature and volume. Assume that the concentrations of the solutions are small; i.e.,
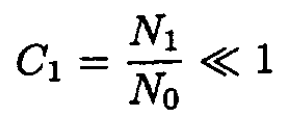
and
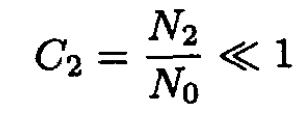
SOLUTION
a) The free energy for a one-component ideal gas is
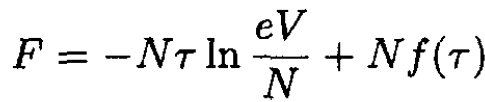 (1)
(1)
The Gibbs free energy
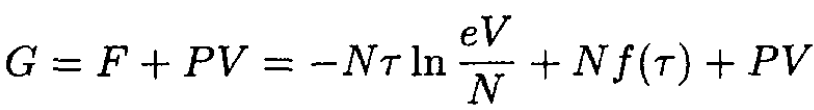 (2)
(2)
But G = G(τ, V, N), so (2) must be transformed:
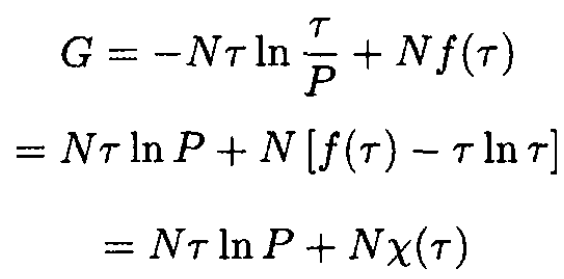 (3)
(3)
If we have a mixture of two types of molecules with N0 and N1 particles each, we find for the thermodynamic potential of the mixture:
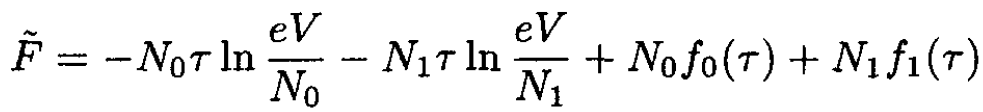 (4)
(4)
Therefore 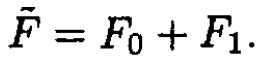 The Gibbs potential of the mixture
The Gibbs potential of the mixture
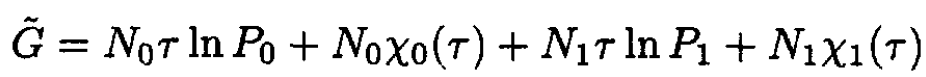 (5)
(5)
where P0, P1 are partial pressures (P = P1 + P2) corresponding to particles A and B, respectively. So,
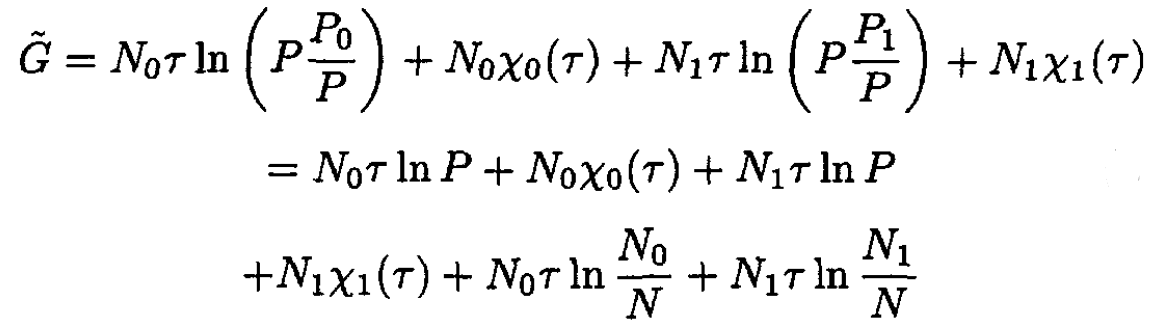 (6)
(6)
It can be seen that
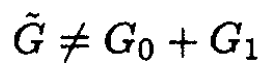
namely
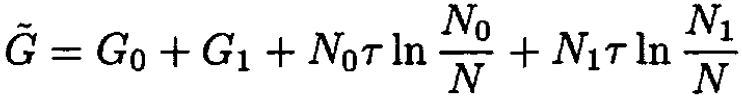 (7)
(7)
where N = N0 + N1.
b) To derive the pressure difference, we notice that for the system with a semipermeable membrane, only the chemical potentials of the solvent are equal, whereas the chemical potentials of the solute do not have to be (since they cannot penetrate through the membrane). We will write first the Gibbs free energy on the left and right of the membrane, 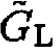 and
and 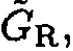 respectively.
respectively.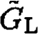 will be defined by (6), with P → PL, whereas
will be defined by (6), with P → PL, whereas
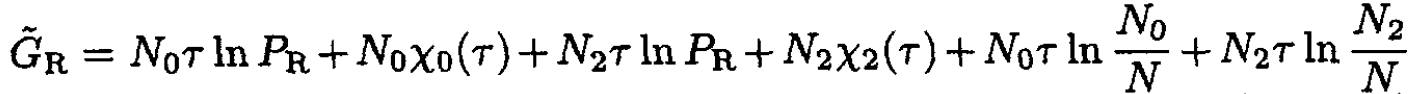 (8)
(8)
The chemical potentials of the solvent are given by
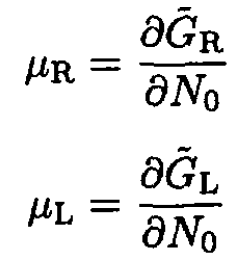 (9)
(9)
Equating μR = μL, we obtain
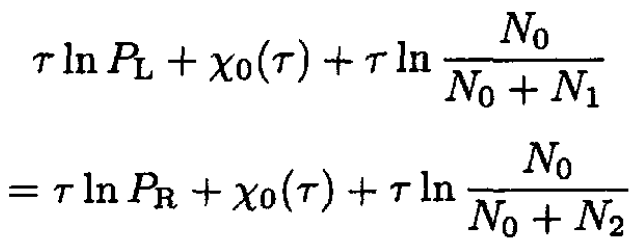 (10)
(10)
or
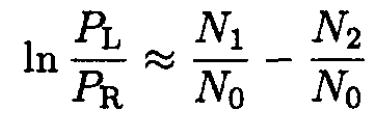 (11)
(11)
where we only take into account the first-order terms in the solute. If we also assume, which is usually the case, that the osmotic pressure is also small, i.e., 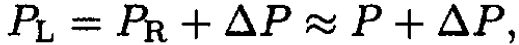 we obtain, from (11),
we obtain, from (11),
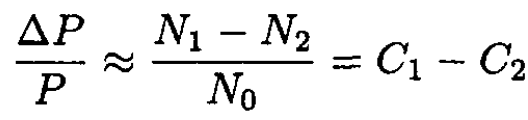 (12)
(12)
where C1 and C2 are the concentrations of the solutes: C1 ≡ N1/N0; C2 ≡ N2/N0. Therefore, with the same accuracy, we arrive at the final formula:
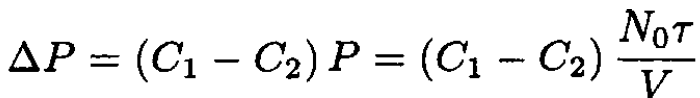 (13)
(13)
A different derivation of this formula may be found in Landau and Lifshitz.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مدرسة دار العلم.. صرح علميّ متميز في كربلاء لنشر علوم أهل البيت (عليهم السلام)
|
|
|