


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 9-8-2016
Date: 11-8-2016
Date: 29-8-2016
|
Charge and Conducting Sphere I
A point charge e is placed at a distance R from the center of a metallic sphere of radius a, with R > a (see Figure 1.1). The sphere is insulated and is electrically neutral.
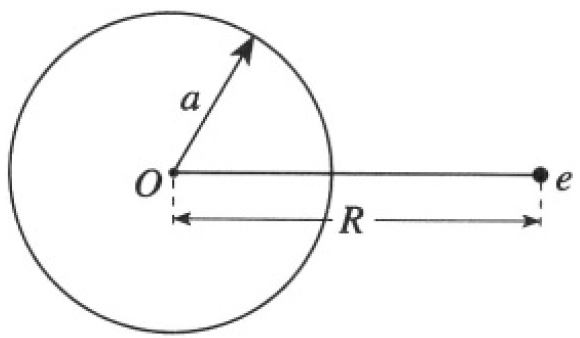
Figure 1.1
a) Find the electrostatic potential on the surface of the sphere.
b) Find the force acting on the charge.
SOLUTION
a) First replace the sphere by an image charge that will create zero potential on the surface of the sphere. We know that is possible to do so with only
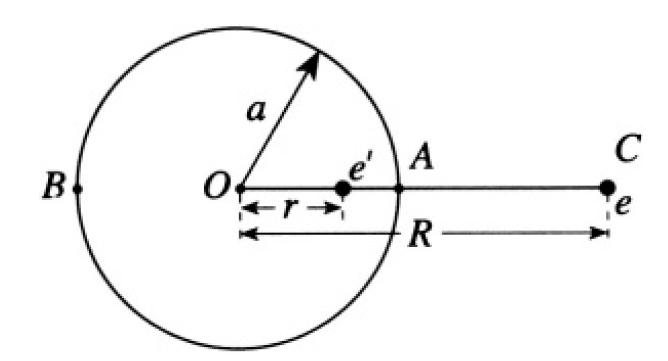
Figure 1.2a
one image charge e' since we can always find a spherical surface of zero potential for two charges. In general, we must consider the potential at arbitrary points on the surface. Consider, for simplicity, two points A and B on opposite sides of a diameter (see Figure 1.2a). The potentials at points A and B due to the two charges e and e' are, respectively,
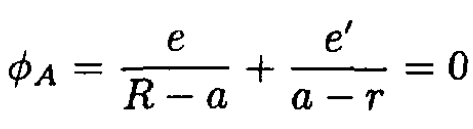 (1)
(1)
and
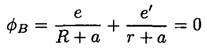 (2)
(2)
or
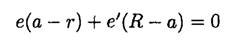 (3)
(3)
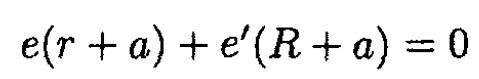 (4)
(4)
From (3) and (4), we can find e' and r
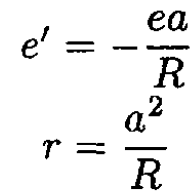
For a neutral sphere, the total charge is constant (Q = 0), so we have to add yet another charge e'' = -e' and at the same time keep the potential constant on the surface of the sphere (see Figure 1.2b). Obviously, we
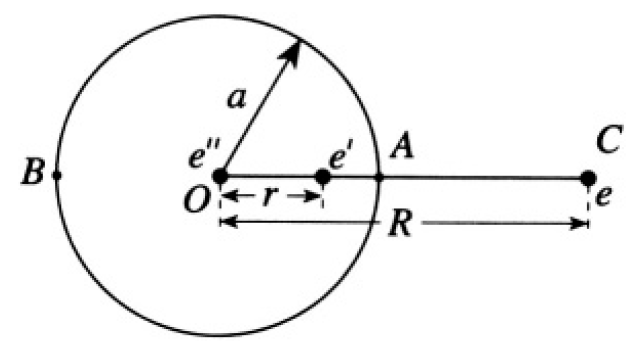
Figure 1.2b
must put this charge at the center of the sphere. The potential on the surface of the sphere is therefore
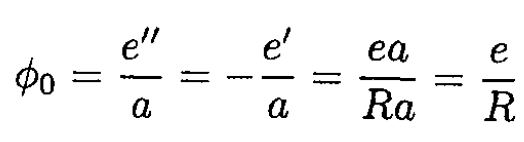
(since the potential due to the other two charges is zero).
b) The force can be found from the interaction between the charge and the two image charges e' and e''. The force is attractive and directed along the radius vector to e.
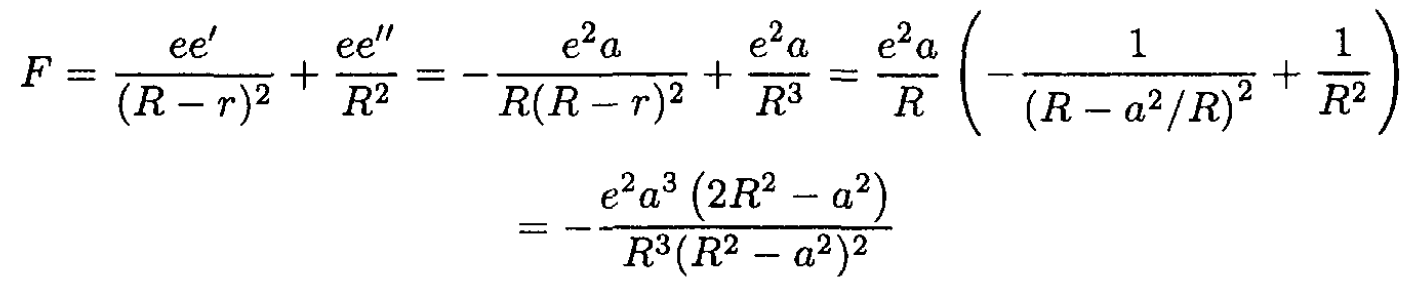



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مدرسة دار العلم.. صرح علميّ متميز في كربلاء لنشر علوم أهل البيت (عليهم السلام)
|
|
|