


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 1-8-2017
Date: 11-8-2017
Date: 3-7-2019
|
THE DIENES
Dienes are aliphatic compounds having two double bonds. When the double bonds are separated by only one single bond, the compound is a conjugated diene (conjugated diolefin). Nonconjugated diolefins have the double bonds separated (isolated) by more than one single bond. This latter class is of little industrial importance. Each double bond in the compound behaves independently and reacts as if the other is not present. Examples of nonconjugated dienes are 1,4-pentadiene and 1,4- cyclo-hexadiene. Examples of conjugated dienes are 1,3-butadiene and 1,3-cyclohexadiene.
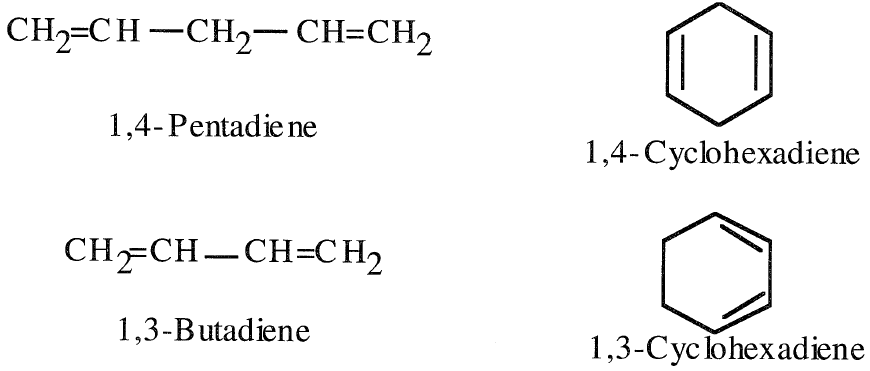
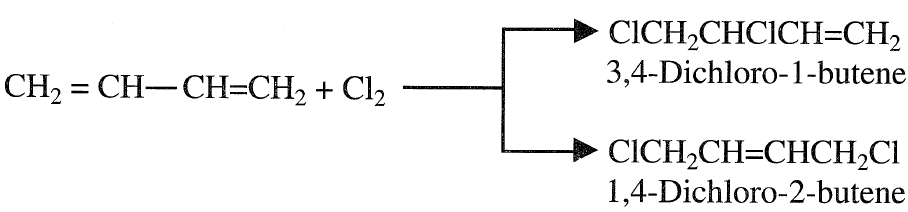
An important difference between conjugated and nonconjugated dienes is that the former compounds can react with reagents such as chlorine, yielding 1,2- and 1,4-addition products. For example, the reaction between chlorine and 1,3-butadiene produces a mixture of 1,4-dichloro- 2-butene and 3,4-dichloro- 1-butene:
When polymerizing dienes for synthetic rubber production, coordination catalysts are used to direct the reaction to yield predominantly 1,4 addition polymers. The following reviews some of the physical and chemical properties of butadiene and isoprene.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مدرسة دار العلم.. صرح علميّ متميز في كربلاء لنشر علوم أهل البيت (عليهم السلام)
|
|
|