


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 28-2-2017
Date: 27-4-2019
Date: 21-7-2020
|
Another Isomerism in Complexes
Another important type of isomers are optical isomers, or enantiomers, in which two objects are exact mirror images of each other but cannot be lined up so that all parts match. This means that optical isomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images. A classic example of this is a pair of hands, in which the right and left hand are mirror images of one another but cannot be superimposed. Optical isomers are very important in organic and biochemistry because living systems often incorporate one specific optical isomer and not the other. Unlike geometric isomers, pairs of optical isomers have identical properties (boiling point, polarity, solubility, etc.). Optical isomers differ only in the way they affect polarized light and how they react with other optical isomers. For coordination complexes, many coordination compounds such as [M(en)3]n+ [in which Mn+ is a central metal ion such as iron(III) or cobalt(II)] form enantiomers, as shown in Figure 1 . These two isomers will react differently with other optical isomers. For example, DNA helices are optical isomers, and the form that occurs in nature (right-handed DNA) will bind to only one isomer of [M(en)3]n+ and not the other.
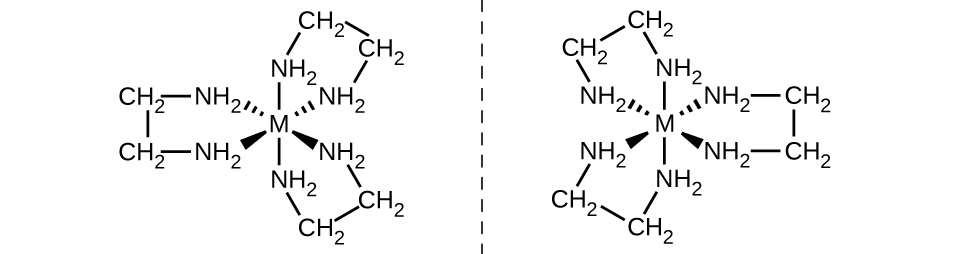
Figure 1 : The complex [M(en)3]n+ (Mn+ = a metal ion, en = ethylenediamine) has a nonsuperimposable mirror image. The [Co(en)2Cl2]+ ion exhibits geometric isomerism (cis/trans), and its cis isomer exists as a pair of optical isomers (Figure 2).

Figure 2 : Three isomeric forms of [Co(en)2Cl2]+ exist. The trans isomer, formed when the chlorines are positioned at a 180° angle, has very different properties from the cis isomers. The mirror images of the cis isomer form a pair of optical isomers, which have identical behavior except when reacting with other enantiomers.
Linkage isomers occur when the coordination compound contains a ligand that can bind to the transition metal center through two different atoms. For example, the CN ligand can bind through the carbon atom (cyano) or through the nitrogen atom (isocyano). Similarly, SCN− can be bound through the sulfur or nitrogen atom, affording two distinct compounds ([Co(NH3)5SCN]2+ or [Co(NH3)5NCS]2+).
Ionization isomers (or coordination isomers) occur when one anionic ligand in the inner coordination sphere is replaced with the counter ion from the outer coordination sphere. A simple example of two ionization isomers are [CoCl6][Br] and [CoCl5Br][Cl].



|
|
|
|
إدارة الغذاء والدواء الأميركية تقرّ عقارا جديدا للألزهايمر
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
شراء وقود الطائرات المستدام.. "الدفع" من جيب المسافر
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ضمن مؤتمر الإمام الحجة(عجل الله فرجه) العلمي باحث كويتي يناقش إثبات ولادة الإمام المهدي (عجّل الله فرجه) من التّوقيعات الشّريفة
|
|
|