


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 29-3-2016
Date: 29-3-2016
Date: 8-10-2017
|
Alzheimer’s Disease
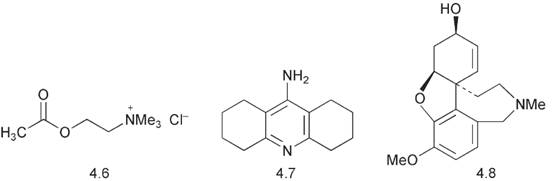
Alzheimer’s disease is a degenerative neurological disease in which the patients increasingly lose their memory and become confused. It is the most common cause of dementia in the elderly. Nerve cells in the brain particularly in the hippocampus and the cerebral cortex, die and the levels of several neurotransmitters including acetylcholine 4.6, fall.
The loss of the nerve cells is accompanied by the formation of bamyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. The plaques are formed from clumps of β-amyloid protein that accumulate in the space between the nerve cells, while the tangles are found inside the nerve cells and are derived from a protein known as tau.
The acetylcholine deficiency cannot be remedied by just giving acetylcholine because it is too polar to cross the blood: brain barrier. Many of the current strategies are aimed at alleviating the symptoms by inhibiting the metabolism of acetylcholine in the brain. Acetylcholine is metabolized by hydrolysis of the acetate ester. Acetylcholine esterase inhibitors that are of value in this connection are tacrine (Cognex®) 4.7, the daffodil alkaloid galanthamine (Reminyl®) 4.8, donepezil hydrochloride (Aricept®) 4.9 and rivastigmine (Exelon®) 4.10. More recent targets have been to prevent th β-amyloid protein undergoing cleavage in a way that initiates the formation of the β-amyloid plaques. This cleavage is brought about by a protease known as β-secretase and a number of compounds have been identified, which inhibit the production of this enzyme. These include the spiroketal antibiotic, monensin.



|
|
|
|
مخاطر عدم علاج ارتفاع ضغط الدم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
البحرين تفوز بجائزة أفضل وجهة للمعارض والمؤتمرات
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مدرسة دار العلم.. صرح علميّ متميز في كربلاء لنشر علوم أهل البيت (عليهم السلام)
|
|
|