
 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 18-1-2016
Date: 18-1-2016
Date: 18-1-2016
|
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
The nervous system has two major divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system that lies outside this (see Scheme 2).
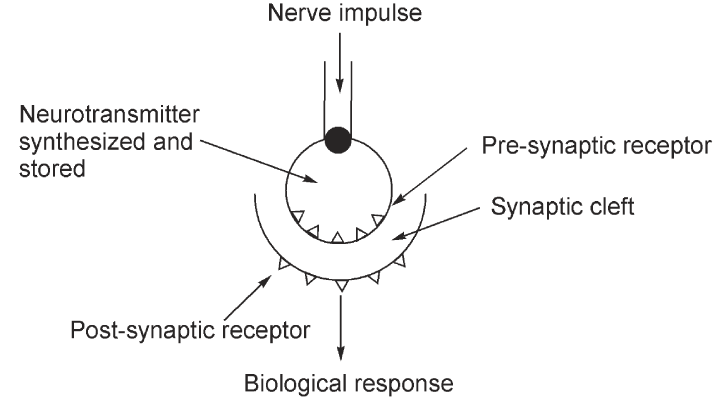
Scheme 1 Schematic diagram of a nerve ending
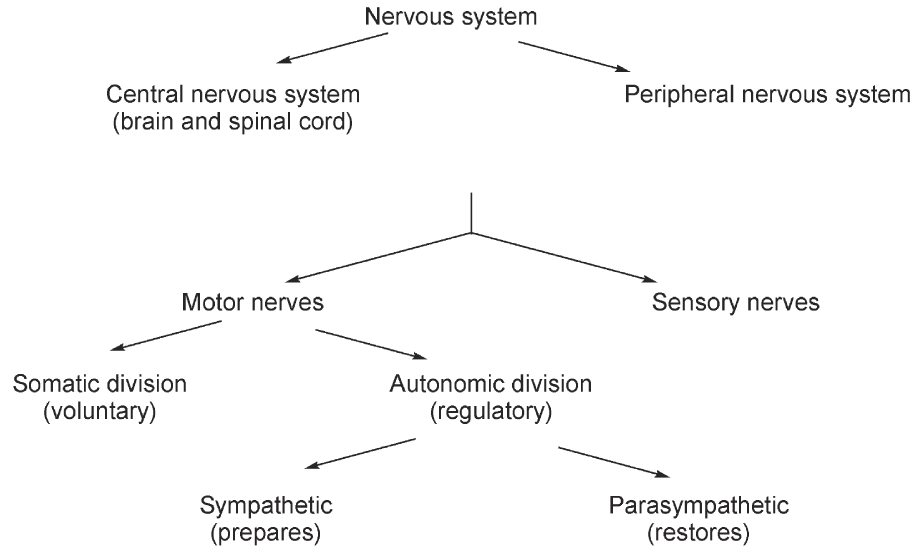
Scheme 2 Divisions of the nervous system
The peripheral nervous system can be divided into the motor (functional) and sensory nerves.
The motor nerves are further sub-divided into the autonomic and somatic nerves. The autonomic nerves regulate the everyday needs ofthe body such as heart function and gastrointestinal motility, without the conscious participation of the brain. The somatic or voluntary system regulates functions such as muscular and skeletal movements under the conscious control of the brain (see Scheme 2).
The autonomic system is further sub-divided into the sympathetic nervous system, which has the role of preparing the muscle for action, for example, to increase heart rate, while the parasympathetic system has the role of restoring the system to a steady state – for example, decreasing heart rate.
The autonomic system has two sections, which are joined by ganglia or a grouping of nerve cells. Transmission of information from the preganglionic to the post-ganglionic section is mediated by a neurotransmitter. The post-ganglionic neuron also uses a second neurotransmitter at the nerve ending. A neurotransmitter is released and crosses the narrow synaptic cleft to bind to a receptor. This binding to the receptor then brings about the effect of the nerve impulse. The voluntary or somatic nervous system differs from the autonomic nervous system by taking the information directly from the CNS to skeletal muscle without the intervention of ganglia.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|