


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 23-7-2017
Date: 3-9-2017
Date: 21-8-2017
|
Ammonia Production (Haber Process)
The production of ammonia is of historical interest because it represents the first important application of thermodynamics to an industrial process. Considering the synthesis reaction of ammonia from its elements, the calculated reaction heat (ΔH) and free energy change (ΔG) at room temperature are approximately –46 and –16.5 KJ/mol, respectively.
Although the calculated equilibrium constant Kc = 3.6 × 108 at room temperature is substantially high, no reaction occurs under these conditions, and the rate is practically zero. The ammonia synthesis reaction could be represented as follows:
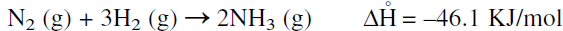
Increasing the temperature increases the reaction rate, but decreases the equilibrium (Kc @ 500°C = 0.08). According to LeChatlier’s principle, the equilibrium is favored at high pressures and at lower temperatures. Much of Haber’s research was to find a catalyst that favored the formation of ammonia at a reasonable rate at lower temperatures. Iron oxide promoted with other oxides such as potassium and aluminum oxides is currently used to produce ammonia in good yield at relatively low temperatures.
In a commercial process, a mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen (exit gas from the methanator) in a ratio of 3:1 is compressed to the desired pressure (150–1,000 atmospheres). The compressed mixture is then preheated by heat exchange with the product stream before entering the ammonia reactor. The reaction occurs over the catalyst bed at about 450°C. The exit gas containing ammonia is passed through a cooling chamber where ammonia is condensed to a liquid, while unreacted hydrogen and nitrogen are recycled. Usually, a conversion of approximately 15% per pass is obtained under these conditions.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|