


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 23-7-2017
Date: 22-8-2017
Date: 3-9-2017
|
THE CLAUS PROCESS
This process includes two main sections: the burner section with a reaction chamber that does not have a catalyst, and a Claus reactor section.
In the burner section, part of the feed containing hydrogen sulfide and some hydrocarbons is burned with a limited amount of air. The two main reactions that occur in this section are the complete oxidation of part of the hydrogen sulfide (feed) to sulfur dioxide and water and the partial oxidation of another part of the hydrogen sulfide to sulfur. The two reactions are exothermic:
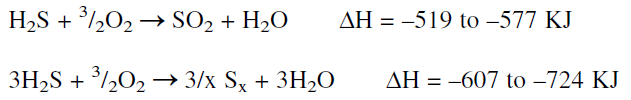
In the second section, unconverted hydrogen sulfide reacts with the produced sulfur dioxide over a bauxite catalyst in the Claus reactor.
Normally more than one reactor is available. In the Super-Claus process (Figure 4-3), three reactors are used. The last reactor contains a selective oxidation catalyst of high efficiency. The reaction is slightly exothermic:
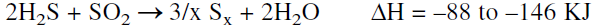
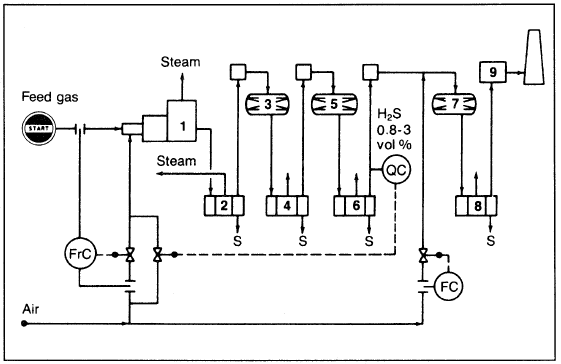
Figure 1.1. The Super Claus process for producing sulfur: (1) main burner, (2,4, 6,8) condensers, (3,5) Claus reactors, (7) reactor with selective oxidation catalyst.
After each reaction stage, sulfur is removed by condensation so that it does not collect on the catalyst. The temperature in the catalytic converter should be kept over the dew point of sulfur to prevent condensation on the catalyst surface, which reduces activity.
Due to the presence of hydrocarbons in the gas feed to the burner section, some undesirable reactions occur, such as the formation of carbon disulfide (CS2) and carbonyl sulfide (COS). A good catalyst has a high activity toward H2S conversion to sulfur and a reconversion of COS and
CS2 to sulfur and carbon oxides. Mercaptans in the acid gas feed results in an increase in the air demand. For example, approximately 5–13%
increase in the air required is anticipated if about 2 mol% mercaptans are present. The increase in the air requirement is essentially a function of the type of mercaptans present. The oxidation of mercaptans could be represented as:
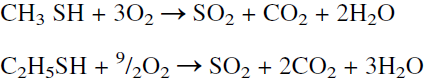
Sulfur dioxide is then reduced in the Claus reactor to elemental sulfur.



|
|
|
|
مخاطر عدم علاج ارتفاع ضغط الدم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اختراق جديد في علاج سرطان البروستات العدواني
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مدرسة دار العلم.. صرح علميّ متميز في كربلاء لنشر علوم أهل البيت (عليهم السلام)
|
|
|