


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 18-5-2017
Date: 20-5-2017
Date: 18-5-2017
|
Probability Function
One postulate used in the derivation of the Fermi-Dirac probability function was the Pauli exclusion principle, which states that only one particle is permitted in each quantum state. The Pauli exclusion principle also applies to the donor and acceptor states.
Suppose we have Ni electrons and gi quantum states, where the subscript i indicates the ith energy level. There are gi ways of choosing where to put the first panicle. Each donor level has two possible spin orientations for the donor electron; thus each donor level has two quantum states. The insertion of an electron into one quantum state, however, precludes putting an electron into the second quantum state. Be adding one electron, the vacancy requirement of the atom is satisfied, and the addition of a second electron in the donor level is not possible. The distribution function of donor electrons in the donor energy states is then slightly different than the Fermi-Dirac function.
The probability function of electrons occupying the donor state is
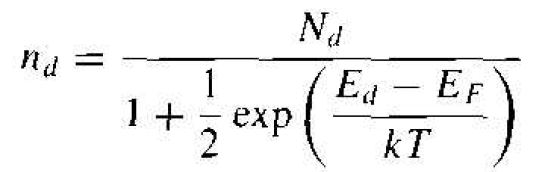 (1)
(1)
where nd is the density of electrons occupying the donor level and Ed is the energy of the donor level. The factor 1/4 in this equation is a direct result of the spin factor just mentioned. The 1/4 factor is sometimes written as l/g, where g is called a degeneracy factor.
Equation (1) can also be written in the form
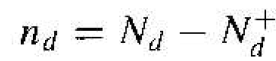 (2)
(2)
where N+d is the concentration of ionized donors. In many applications, we will be interested more in the concentration of ionized donors than in the concentration of electrons remaining in the donor states.
If we do the same type of analysis for acceptor atoms, we obtain the expression
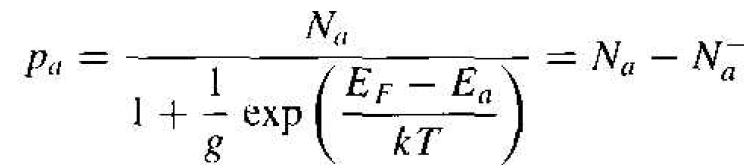 (3)
(3)
where Na is the concentration of acceptor atoms, Ea is the acceptor energy level, pa is the concentration of holes in the acceptor states, and N-a is the concentration of ionized acceptors. A hole in an acceptor state corresponds to an acceptor atom that is neutrally charged and still has an "empty" bonding position. The parameter g is, again, a degeneracy factor. The ground state degeneracy factor g is normally taken as four for the acceptor level in silicon and gallium arsenide because of the detailed band structure.



|
|
|
|
4 أسباب تجعلك تضيف الزنجبيل إلى طعامك.. تعرف عليها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
الفلبين.. بركان "كانلاون" يطلق عمودا من الرماد بارتفاع 4 كم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أصواتٌ قرآنية واعدة .. أكثر من 80 برعماً يشارك في المحفل القرآني الرمضاني بالصحن الحيدري الشريف
|
|
|