


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 21-8-2016
Date: 28-7-2016
Date: 25-7-2016
|
Diatomic Molecules in Three Dimensions
Consider the free rotation of a diatomic molecule consisting of two atoms of mass m1 and m2, respectively, separated by a distance a. Assume that the molecule is rigid with center of mass fixed.
a) Starting from the kinetic energy εk, where
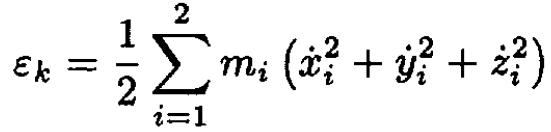
derive the kinetic energy of this system in spherical coordinates and show that
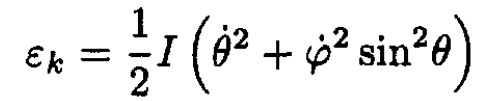
where I is the moment of inertia. Express I in terms of m1, m2, and a.
b) Derive the canonical conjugate momenta pθ and pφ. Express the Hamiltonian of this system in terms of pθ, pφ, θ, φ, and I.
c) The classical partition function is defined as
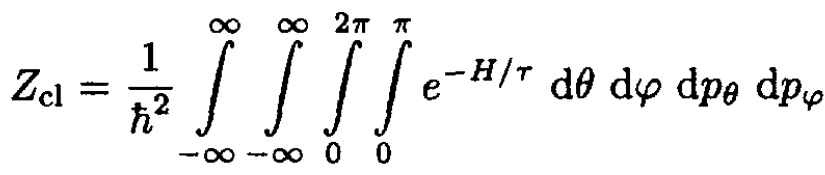
Calculate Zcl. Calculate the heat capacity for a system of N molecules.
d) Assume now that the rotational motion of the molecule is described by quantum mechanics. Write the partition function in this case, taking into account the degeneracy of each state. Calculate the heat capacity of a system of N molecules in the limit of low and high temperatures and compare them to the classical result.
SOLUTION
a) We first transform the expression of the kinetic energy εk:
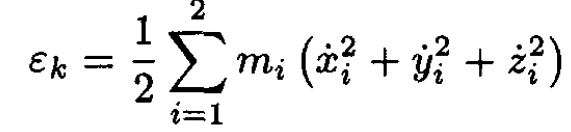 (1)
(1)
where xi, yi, zi are the Cartesian coordinates of the molecule in the frame with the c.m. at the origin to spherical coordinates:
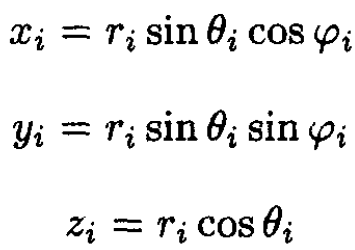 (2)
(2)
For the rigid diatom,
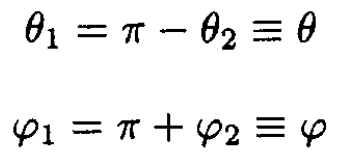
We may substitute (2) into (1), obtaining
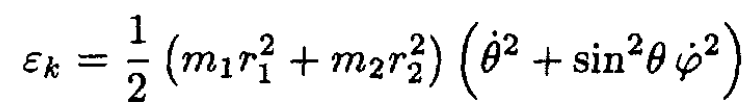 (3)
(3)
Using the definition of c.m., we may write
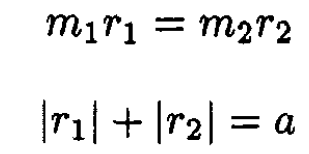 (4)
(4)
yielding
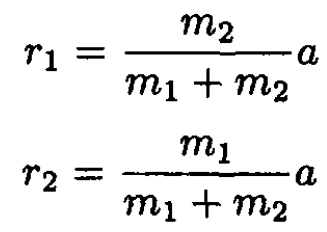 (5)
(5)
Then (3) becomes
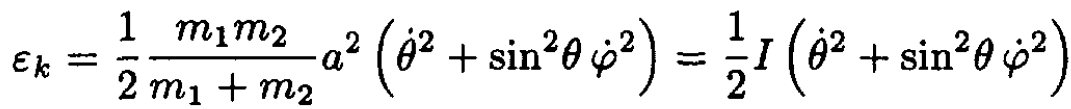 (6)
(6)
with
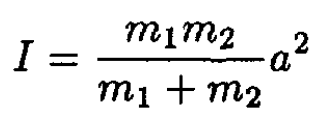
b) In order to find the conjugate momenta pθ, pφ, we must compute the Lagrangian
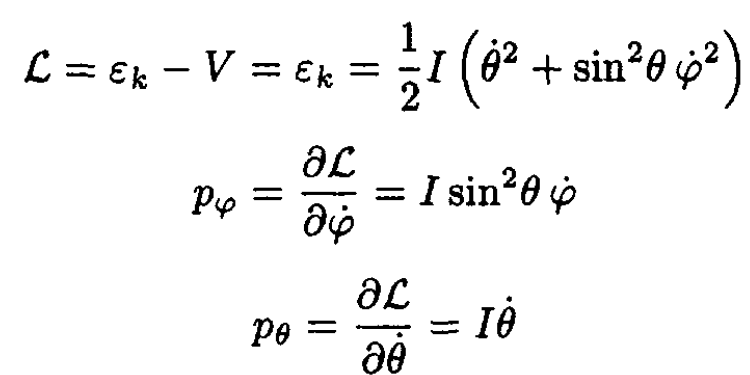 (7)
(7)
Expressing 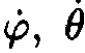 through pφ, pθ
through pφ, pθ

we may rewrite the Hamiltonian as
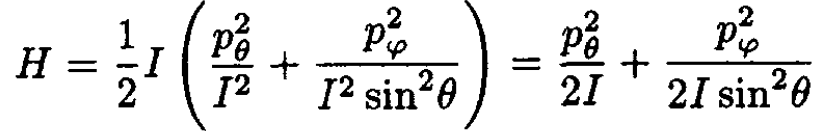 (8)
(8)
c) The single-diatom partition function may be computed as follows:
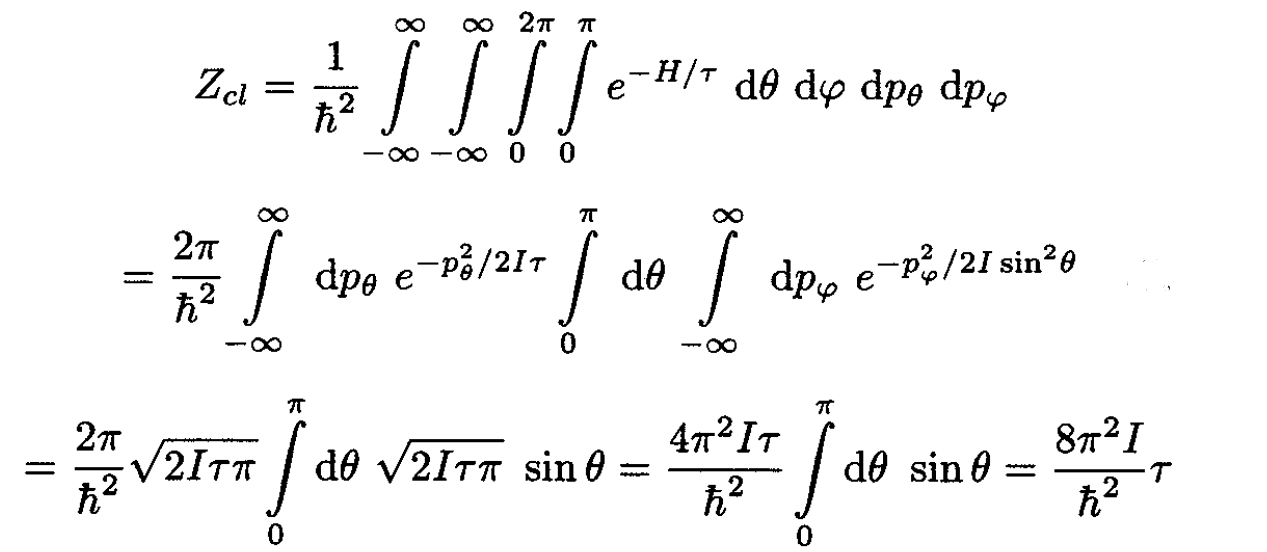 (9)
(9)
Now the free energy F for N such classical molecules may be found from
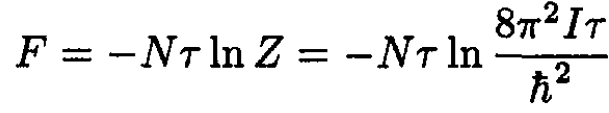 (10)
(10)
The entropy S is then
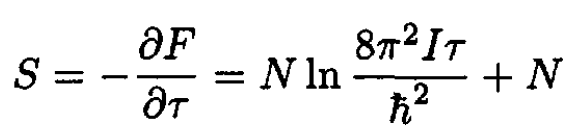 (11)
(11)
and the energy E and heat capacity C are
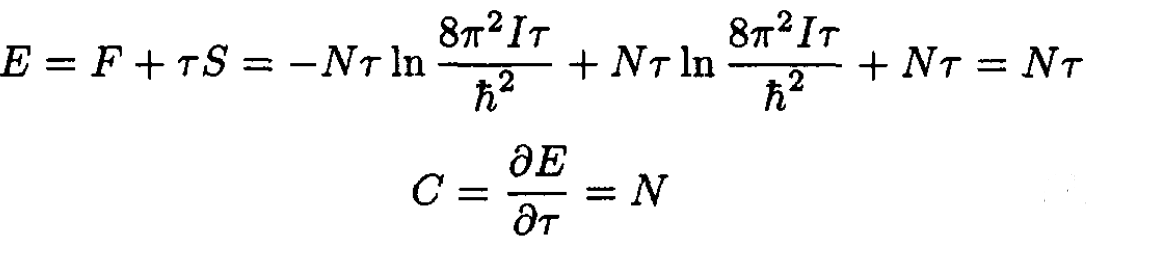 (12)
(12)
d) For the quantum case the Schrodinger equation for a rigid rotator
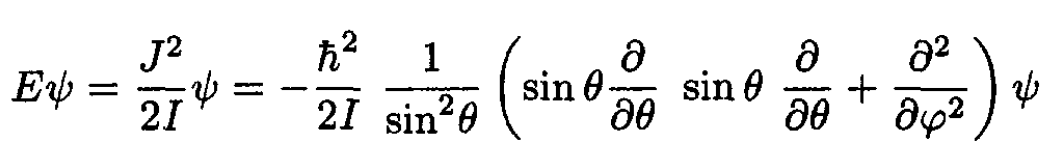 (13)
(13)
admits the standard solution
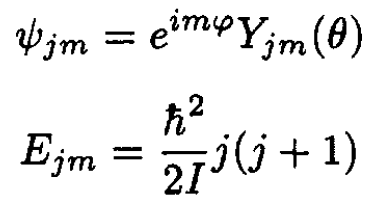 (14)
(14)
where each of the energy states is (2j + 1)-degenerate. The partition function Zq is given by
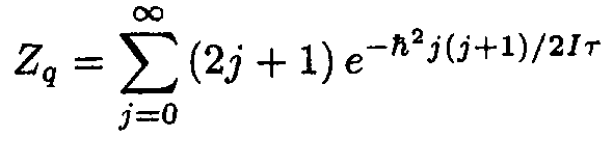 (15)
(15)
For low temperatures we may neglect high-order terms and write
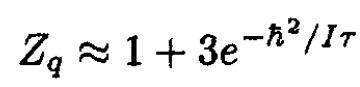
where we left only terms with j = 0 and j = 1. For N molecules we find for the free energy that
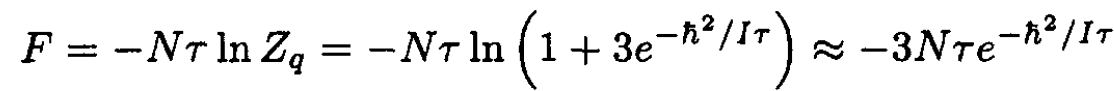 (16)
(16)
The energy E and heat capacity C are then
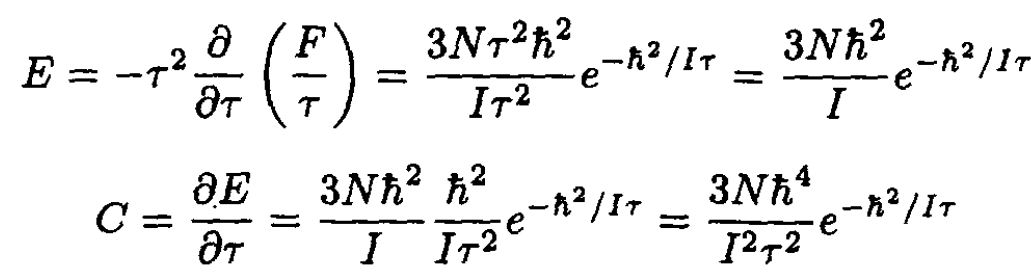 (17)
(17)
So, at low temperatures the heat capacity corresponding to the rotational degrees of freedom is exponentially small. This implies that there would be no difference, in this limit, between the heat capacity for monatomic and diatomic molecules. In the opposite case, at high temperatures, h2/2I << τ, the sum may be replaced by an integral:
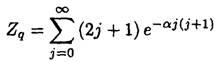 (18)
(18)
where α ≡ h2/2I τ. Proceeding from (18), we have
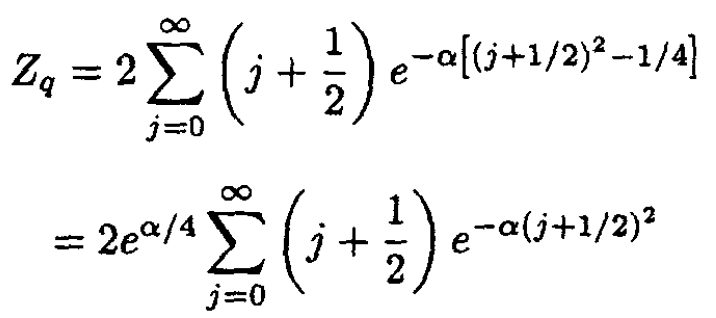 (19)
(19)
Replacing the sum by an integral, we obtain
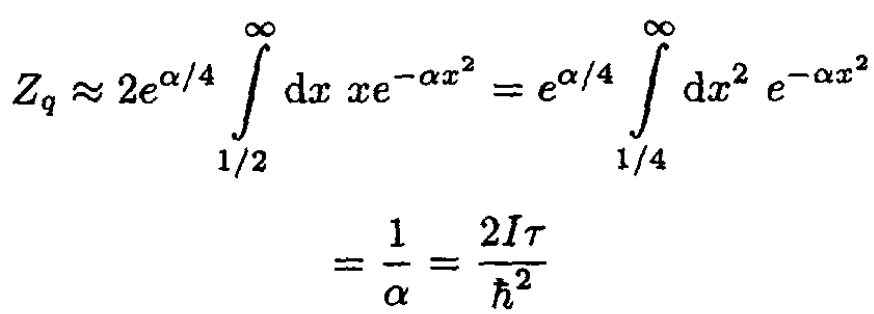 (20)
(20)
Therefore, in the classical limit (high temperatures),
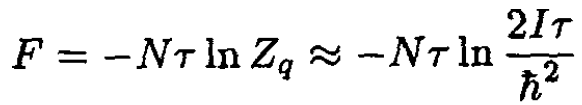 (21)
(21)
The energy E and heat capacity C are given by
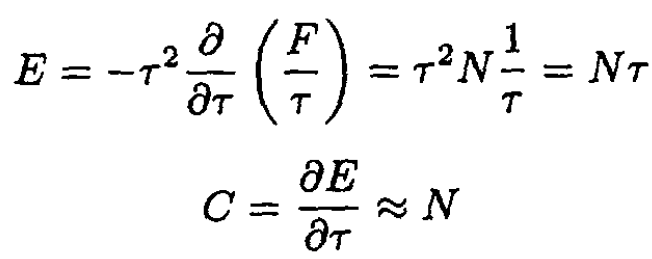 (22)
(22)
We see that this is the same as found in (12). Since we expect a heat capacity per degree of freedom of 1/2, we see that there are two degrees of freedom for each molecule since
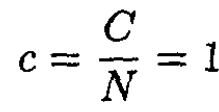
They correspond to the two rotational degrees of freedom of a classical rod. (There are no spatial degrees of freedom since the molecule is considered fixed.)



|
|
|
|
مخاطر عدم علاج ارتفاع ضغط الدم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اختراق جديد في علاج سرطان البروستات العدواني
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مدرسة دار العلم.. صرح علميّ متميز في كربلاء لنشر علوم أهل البيت (عليهم السلام)
|
|
|