


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
أقرأ أيضاً
التاريخ: 2024-02-28
التاريخ: 23-1-2020
التاريخ: 20-8-2019
التاريخ: 22-11-2019
|
Many secondary and tertiary halides undergo E1 elimination in competition with the SN1 reaction in neutral or acidic solutions. For example, when tert-butyl chloride solvolyzes in 80% aqueous ethanol at 25o, it gives 83% tert-butyl alcohol by substitution and 17% 2-methylpropene by elimination:
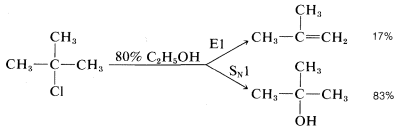
The ratio of substitution and elimination remains constant throughout the reaction, which means that each process has the kinetic order with respect to the concentration of tert-butyl halide. The SN1 and E1 reactions have a common rate-determining step, namely, slow ionization of the halide. The solvent then has the choice of attacking the intermediate carbocation at the positive carbon to effect substitution, or at a β hydrogen to effect elimination:
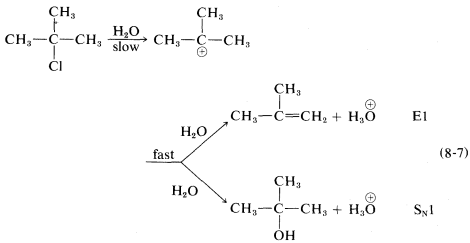
Factors influencing the E1 reactions are expected to be similar to those for the SN1 reactions. An ionizing solvent is necessary, and for easy reaction the RX compound must have a good leaving group and form a relatively stable R⊕ cation. Therefore the E1 orders of reaction rates are X=I > Br >Cl > F and tertiary R > secondary R > primary R.
With halides such as 2-chloro-2-methylbutane, which can give different alkenes depending on the direction of elimination, the E1 reaction is like the E2 reaction in tending to favor the most stable or highly substituted alkene:
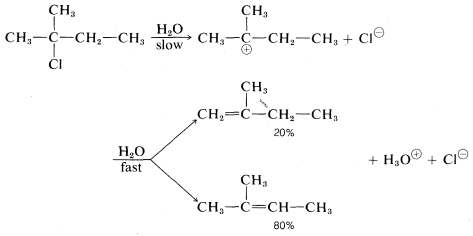



|
|
|
|
"إنقاص الوزن".. مشروب تقليدي قد يتفوق على حقن "أوزيمبيك"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
الصين تحقق اختراقا بطائرة مسيرة مزودة بالذكاء الاصطناعي
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ووفد من جامعة البصرة يبحثان سبل تعزيز التعاون المشترك
|
|
|