


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
أقرأ أيضاً
التاريخ: 21-8-2016
التاريخ: 16-10-2019
التاريخ: 1-9-2019
التاريخ: 23-12-2021
|
Two simple mechanisms can be written for the reaction of chloromethane with hydroxide ion in aqueous solution that differ in the timing of bond breaking relative to bond making. In the first mechanism, A, the overall reaction is the result of two steps, the first of which involves a slow dissociation of chloromethane to solvated methyl carbocation 4 and solvated chloride ion. The second step involves a fast reaction between the carbocation and hydroxide ion (or water) to yield methanol.
Mechanism A:
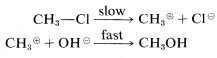
or
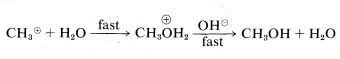
In the second mechanism, B, the reaction proceeds in a single step. Attack of hydroxide ion at carbon occurs simultaneously with the loss of chloride ion; that is, the carbon-oxygen bond is formed as the carbon-chlorine bond is broken:
Mechanism B:
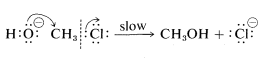
Both of these mechanisms are important in the displacement reactions of alkyl compounds, although chloromethane appears to react only by Mechanism BB. Now we will discuss the criteria for distinguishing between the concerted and stepwise mechanisms.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مدرسة دار العلم.. صرح علميّ متميز في كربلاء لنشر علوم أهل البيت (عليهم السلام)
|
|
|