


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 18-4-2021
Date: 25-4-2021
Date: 5-5-2021
|
Drive and overdrive
Class-A power amplifiers do not, in theory, take any power from the signal source in order to produce a significant amount of output power. This is one of the advantages of class-A operation. The same is true for class-AB1 amplifiers. It is only necessary that a certain voltage be present at the control electrode (the base, gate, emitter, or source). Class-AB2 amplifiers need some driving power to produce ac power output. Class-B amplifiers require more drive than class-AB2, and class-C amplifiers need still more drive.
Whatever kind of PA is used in a given situation, it is important that the driving signal not be too strong. If overdrive takes place, there will be distortion in the output signal. An oscilloscope can be used to determine whether or not an amplifier is being overdriven. The scope is connected to the amplifier output terminals, and the waveshape of the output signal is examined. The output waveform for a particular class of amplifier always has a characteristic shape. Overdrive is indicated by a form of distortion known as flat topping.
In Fig. 1A, the output signal waveshape for a properly operating class-B amplifier is shown. It looks like the output of a half-wave rectifier, because the bipolar transistor or FET is drawing current for exactly half (180 degrees) of the cycle.
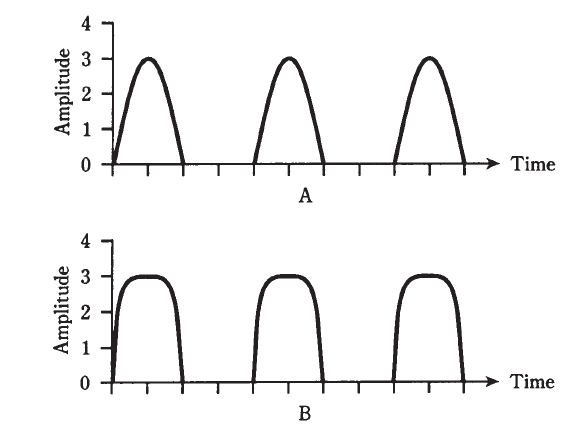
Fig. 1: At A, waveshape at the output of a properly operating class-B amplifier. At B, distortion in the output waveshape caused by overdrive.
In Fig. 1B, the output of an overdriven class-B amplifier is shown. The wave is no longer a half sine wave, but instead, it shows evidence of flat topping. The peaks are blunted or truncated. The result of this is audio distortion in the modulation on a radio signal, and also an excessive amount of energy at harmonic frequencies. The efficiency of a circuit can be degraded by overdrive. The “flat tops” of the distorted waves don’t contribute anything to the strength of the signal at the desired frequency.
But they do cause a higher-than-normal PC or PD value, which translates into a lower-than-normal efficiency Pout/PC or Pout/PD.
A thorough discussion of overdrive and distortion in various amplifier classes and applications would require an entire book. If you’re interested in more detail, a good college or trade-school text on radio-frequency (RF) amplification is recommended.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
وفد كلية الزراعة في جامعة كربلاء يشيد بمشروع الحزام الأخضر
|
|
|