


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 25-2-2016
Date: 27-8-2020
Date: 22-8-2020
|
The cause of precession
Although Hipparchus discovered the phenomena caused by precession in the 2nd century BC, almost two millennia had to elapse before Newton gave an explanation. Newton showed that it was due to the gravitational attractions of Sun and Moon on the rotating, non-spherical Earth. Newton argued on the following lines. If the Earth was perfectly spherical or if the Sun and Moon always moved in the plane of the celestial equator, their net gravitational attractions would act along lines joining these bodies to the Earth’s centre and so would produce no tendency to tilt the Earth’s rotational axis.
The situation is quite different, however. Not only is the Earth an oblate spheroid with an equatorial bulge but both Sun and Moon move in apparent orbits inclined to the plane of the Earth’s equator. Let us consider the Sun. Its orbital plane is the plane of the ecliptic. Because of the asymmetry of the gravitational forces acting upon the Earth’s particles of matter, the resultant solar attraction does not pass through the Earth’s centre C but acts along the line DF (see figure 1). If the Earth were non-rotating, this force would, in time, tilt the planet until the equator and the ecliptic planes coincided. The Earth behaves, however, like a spinning-top. The spinning-top’s weight W acts vertically downwards through its centre of mass G. The axis of spin AB precesses about the vertical AV, always moving at right angles to the plane instantaneously defined by AB and AV so that the top precesses, its spin-axis sweeping out a cone (see figure 2).
In the case of the Earth, the resultant gravitational pull of the Sun acting along DF causes the Earth’s axis of rotation QP to sweep out a precessional cone of axis CK, CK being the direction to the north pole of the ecliptic, K. The north celestial pole, therefore, traces out a small circle about K, of radius ε, in the precessional period of 26 000 years.

Figure 1. The gravitational pull of the Sun on the non-spherical Earth.
The effect of the Sun is complicated by the fact that not only is the Sun’s angular distance above the plane of the equator changing throughout the year but its orbit is elliptical so that its gravitational pull varies. The complete analytical description of the Sun’s precessional effect is, therefore, very complicated.
The Moon’s effect is more complex still but, because its orbit is inclined at only a few degrees to the plane of the ecliptic, its main contribution to precession is similar to that of the Sun. The uniform motion of the north celestial pole along the small circle about the north pole of the ecliptic due to the combined effects of Sun and Moon is called luni-solar precession. As we have seen, this produces a continuous movement of 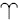 along the ecliptic at a rate of 50''·2 per annum (the modern value) and a corresponding movement of the celestial equator.
along the ecliptic at a rate of 50''·2 per annum (the modern value) and a corresponding movement of the celestial equator.
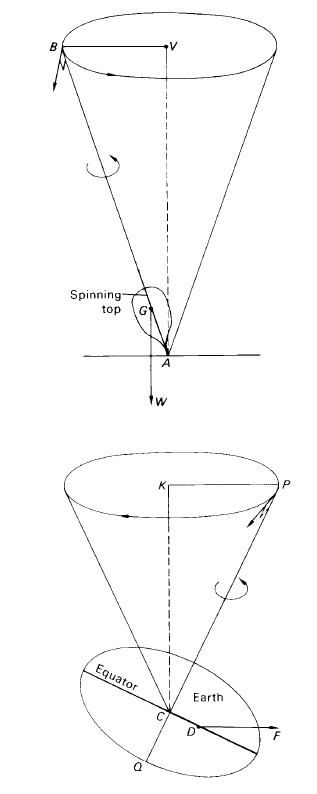
Figure 2. The conical movement of a spinning top compared with the precession of the Earth’s pole.



|
|
|
|
كيف تعزز نمو الشعر الصحي؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 فحوصات مهمة يجب القيام بها لسيارتك قبل الصيف
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الزهراء (عليها السلام) تكرم قسم الشؤون الفكرية بمناسبة اليوم العالمي للكتاب
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف يقيم ندوة علمية حول جهود علماء البصرة في نشر الحديث
|
|
|
|
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يختتم برنامجاً ثقافياً لوفدٍ من جامعة البصرة
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تعقد ورشة عمل عن إجراءات عمل اللجان الامتحانيّة
|