


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية | Elimination-Addition Mechanism of Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution. Arynes |
|
|
|
Read More
Date: 27-11-2019
Date: 3-12-2015
Date: 30-10-2019
|
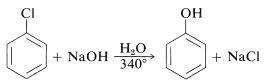
The reactivities of aryl halides, such as the halobenzenes, are exceedingly low toward nucleophilic reagents that normally effect displacements with alkyl halides and activated aryl halides. Substitutions do occur under forcing conditions of either high temperatures or very strong bases. For example, chlorobenzene reacts with sodium hydroxide solution at temperatures around 340o
and this reaction was once an important commercial process for the production of benzenol (phenol):
In addition, aryl chlorides, bromides, and iodides can be converted to areneamines ArNH2 by the conjugate bases of amines. In fact, the reaction of potassium amide with bromobenzene is extremely rapid, even at temperatures as low as −33o with liquid ammonia as solvent:
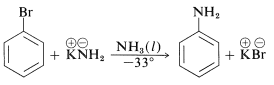
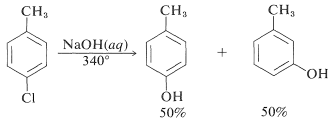
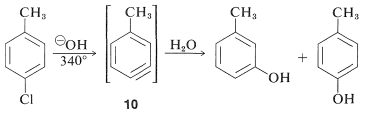
However, displacement reactions of this type differ from the previously discussed displacements of activated aryl halides in that rearrangement often occurs. That is, the entering group does not always occupy the same position on the ring as that vacated by the halogen substituent. For example, the hydrolysis of 4-chloromethylbenzene at 340o
gives an equimolar mixture of 3- and 4-methylbenzenols:
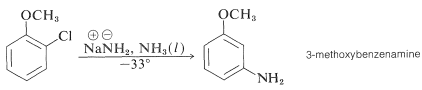
Even more striking is the exclusive formation of 3-methoxybenzenamine in the amination of 2-chloromethoxybenzene. Notice that this result is a violation of the principle of least structural change (Section 1-1H):
The mechanism of this type of reaction has been studied extensively, and much evidence has accumulated in support of a stepwise process, which proceeds first by base-catalyzed elimination of hydrogen halide (HX)
from the aryl halide - as illustrated below for the amination of bromobenzene:
Elimination
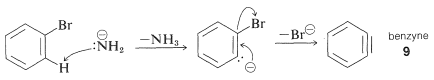
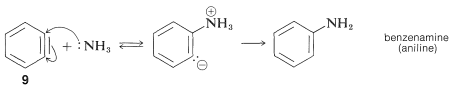
The product of the elimination reaction is a highly reactive intermediate 9
called benzyne, or dehydrobenzene, which differs from benzene in having two less hydrogen and an extra bond between two ortho carbons. Benzyne reacts rapidly with any available nucleophile, in this case the solvent, ammonia, to give an addition product:
Addition
The rearrangements in these reactions result from the attack of the nucleophile at one or the other of the carbons of the extra bond in the intermediate. With benzyne the symmetry is such that no rearrangement would be detected. With substituted benzynes isomeric products may result. Thus 4-methylbenzyne, 10
, from the reaction of hydroxide ion with 4-chloro-1-methylbenzene gives both 3- and 4-methylbenzenols:
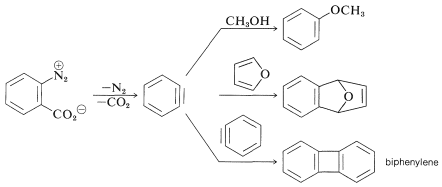
In the foregoing benzyne reactions the base that produces the benzyne in the elimination step is derived from the nucleophile that adds in the addition step. This need not always be so, depending on the reaction conditions. In fact, the synthetic utility of aryne reactions depends in large part of the success with which the aryne can be generated by one reagent but captured by another. One such method will be discussed in Section 14-10C and involves organometallic compounds derived from aryl halides. Another method is to generate the aryne by thermal decomposition of a 1,2-disubstituted arene compound such as 11, in which both substituents are leaving groups - one leaving with an electron pair, the other leaving without:
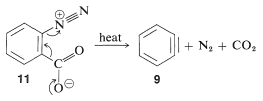
When 11 decomposes in the presence of an added nucleophile, the benzyne intermediate is trapped by the nucleophile as it is formed. Or, if a conjugated diene is present, benzyne will react with it by a [4 + 2] cycloaddition. In the absence of other compounds with which it can react, benzyne will undergo [2 + 2] cycloaddition to itself:



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|