

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Chiral Amines as Resolving Agents and Resolution of Racemic Acids
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
7-7-2019
2087
Chiral Amines as Resolving Agents and Resolution of Racemic Acids
The most commonly used procedure for separating enantiomers is to convert them to a mixture of diastereomers that will have different physical properties: melting point, boiling point, solubility, and so on . For example, if you have a racemic or D,L mixture of enantiomers of an acid and convert this to a salt with a chiral base having the D configuration, the salt will be a mixture of two diastereomers, (D acid . D base) and (L acid . D base). These diastereomeric salts are not identical and they are not mirror images. Therefore they will differ to some degree in their physical properties, and a separation by physical methods, such as crystallization, may be possible. If the diastereomeric salts can be completely separated, the acid regenerated from each salt will be either exclusively the D or the L enantiomer:
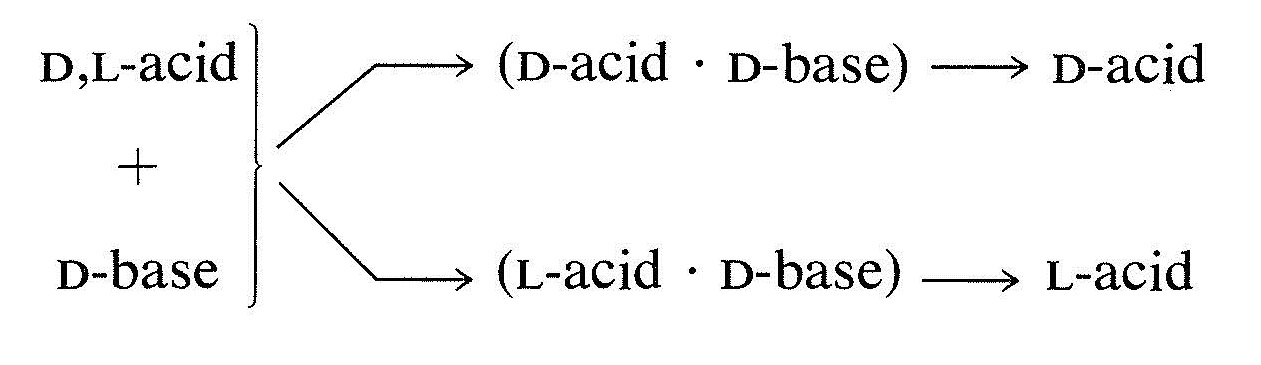
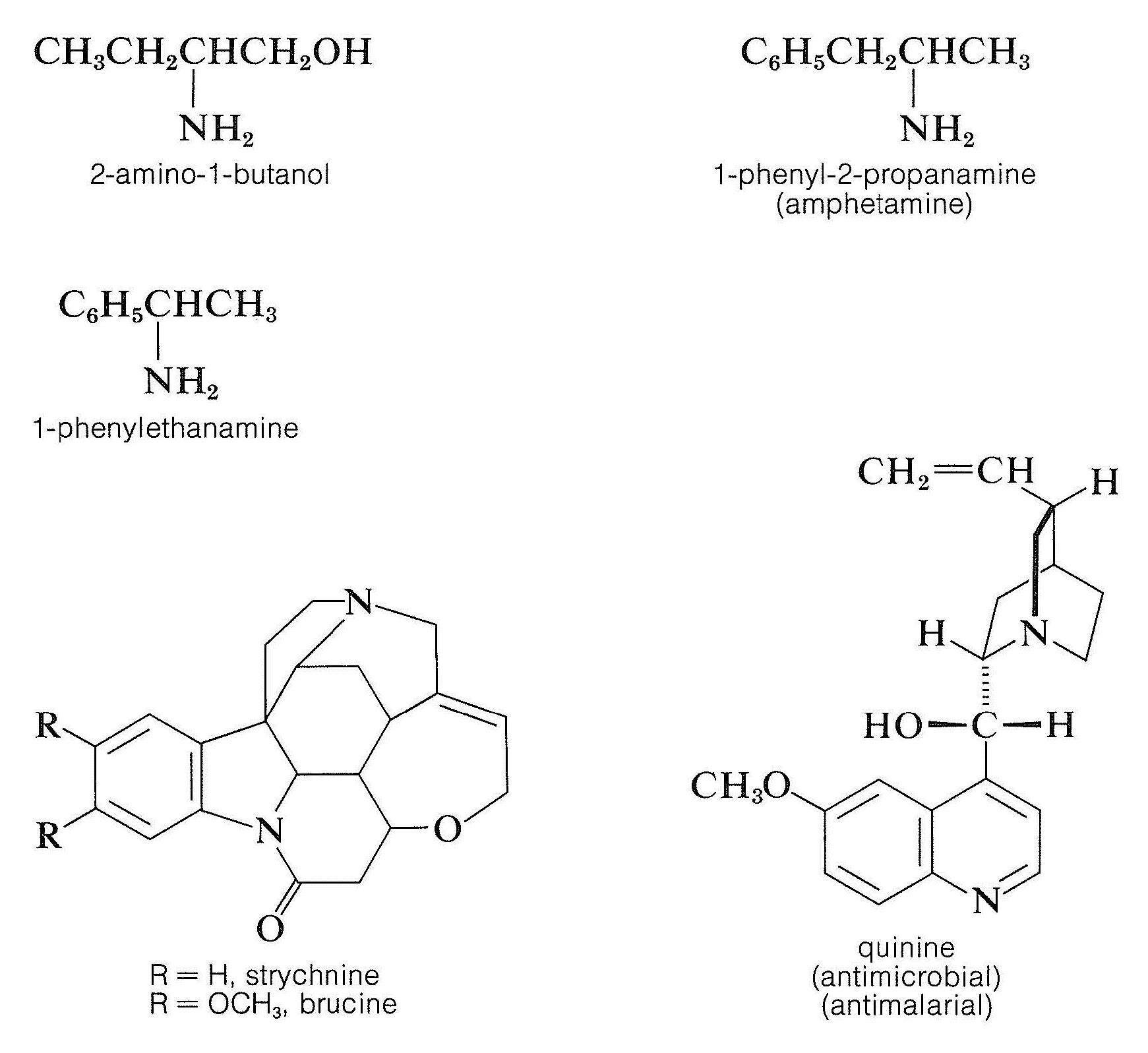
Resolution of chiral acids through the formation of diastereomeric salts requires adequate supplies of suitable chiral bases. Brucine, strychnine, and quinine frequently are used for this purpose because they are readily available, naturally occurring chiral bases. Simpler amines of synthetic origin, such as 2-amino- 1 -butanol, amphetamine, and 1 -phenylethanamine, also can be used, but first they must be resolved themselves.
 الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















