
Innervation
 المؤلف:
Kelly M. Harrell and Ronald Dudek
المؤلف:
Kelly M. Harrell and Ronald Dudek
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Anatomy
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Anatomy
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 18-7-2021
18-7-2021
 2028
2028
Innervation
Innervation of pelvic and perinea! structures can be divided into somatic and autonomic origin. Pelvic floor and perineal musculature and skin receive somatic innervation, while pelvic viscera receive autonomic innervation.
A. Somatic innervation
Muscle and skin of the pelvic floor (diaphragm), pelvic wall, and perineum receive somatic innervation that arises from the sacral plexus (Figs. 1and 2) The sacral plexus is made up of anterior rami from S1-S4 and receives contributions from lumbar spinal nerves by way of the lumbosacral trunk (Lcl5).Two important branches in this region are the pudendal nerve and the nerves to levator ani and coccygeus.
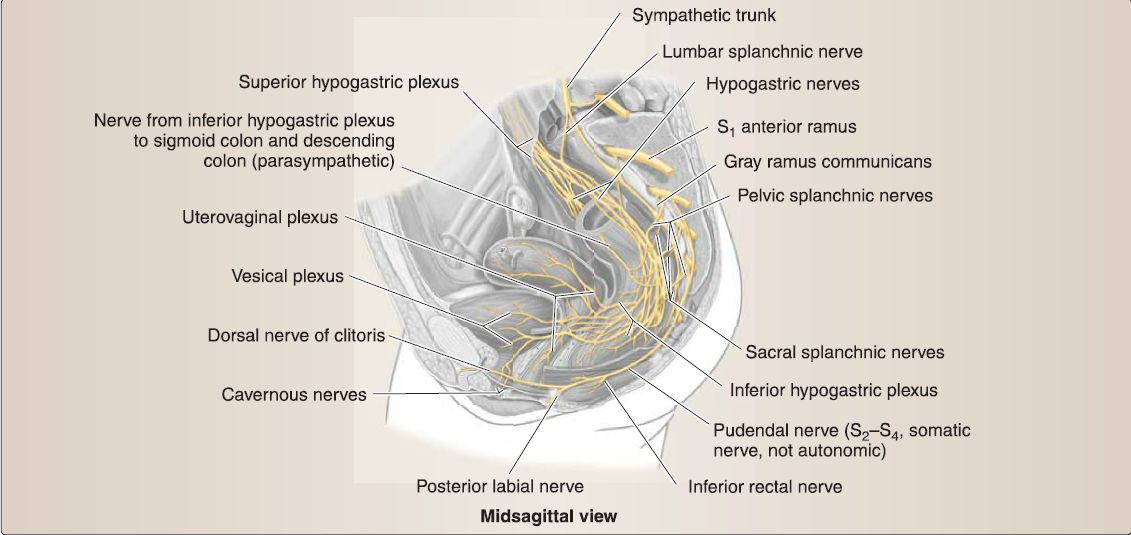 Figure 1: Female pelvic autonomic innervation.
Figure 1: Female pelvic autonomic innervation.
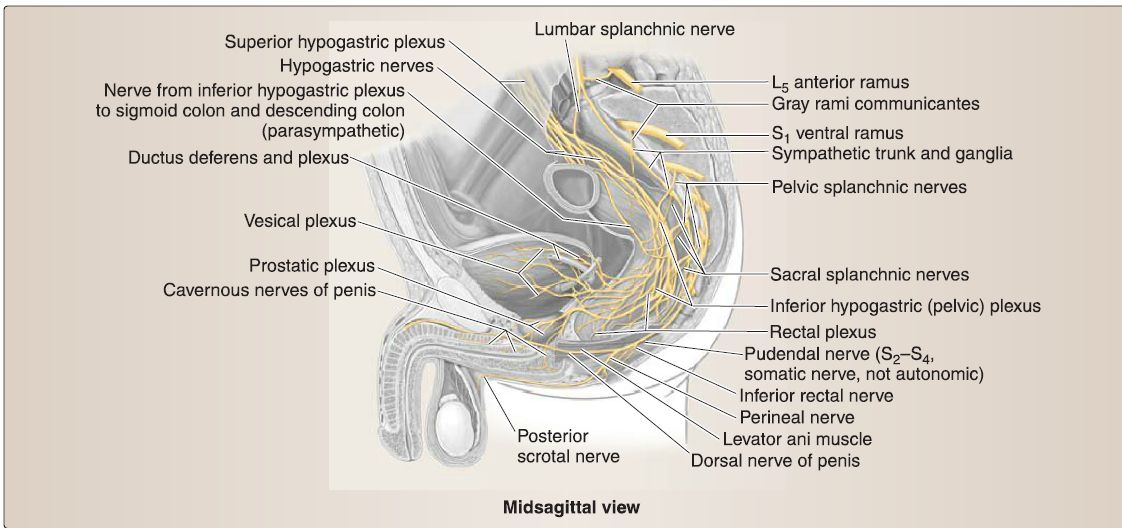 Figure 2: Male pelvic autonomic innervation.
Figure 2: Male pelvic autonomic innervation.
1. Pudenda! nerve: The pudenda! nerve arises from 82-84 anterior rami. It provides motor and sensory innervation to structures of the perineum, including genital sensation and voluntary motor control of external anal and urethral sphincters (see 1, and 2). Branches of the pudenda! nerve include inferior rectal and perineal nerves.
2. Nerves to levator ani and coccygeus: These nerves arise from 83-84 anterior rami. They provide motor innervation to the pelvic (diaphragm) floor musculature. Additional details about contributions to the lower limb from the sacral plexus .
B. Autonomic innervation
Pelvic viscera and perinea! vasculature are controlled by parasympathetic and sympathetic autonomic plexuses (see Figs. 1and 2). Primarily, preganglionic parasympathetic and sympathetic fibers merge to form the inferior hypogastric plexus, which is located bilaterally around the rectum, bladder, and cervix/prostate and extends distally along arterial vasculature to reach adjacent viscera. Subsidiary plexuses are named by the viscera they serve (e.g., prostatic plexus).
1. Sympathetic: Sympathetic preganglionic fibers from lumbar splanchnic nerves travel through the superior hypogastric plexus and hypogastric nerves before joining the inferior hypogastric plexus. In most cases, these fibers synapse in ganglia within the inferior hypogastric plexus and then distribute to viscera via arteries. Sympathetic stimulation drives closure of sphincters, ejaculation, and orgasm. This includes coordinated closure of internal urethral sphincter during ejaculation, to prevent retrograde flow of semen into the bladder. Sympathetic afferent fibers mediate sensation from the uterine fundus and body and superior surface of the bladder. Sympathetic fibers will also join sacral and coccygeal spinal nerves by way of the gray rami communicantes of the sacral sympathetic trunks. These fibers distribute to posterior and anterior rami in this region.
2. Parasympathetic: Parasympathetic preganglionic fibers from pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2-S4) exit the spinal nerves to join the inferior hypogastric plexus. These fibers generally synapse on postganglionic neurons in visceral walls. Parasympathetic stimulation drives opening of sphincters, bladder emptying, erection, and sexual excitation. Aside from the uterine fundus and body and superior bladder, autonomic afferent fibers mediate sensation from pelvic viscera. Therefore, pain sensation from viscera typically travels back to the origin of pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2-S4).
 الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


