

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
The Trachea
المؤلف:
Harold Ellis,Vishy Mahadevan
المصدر:
Clinical Anatomy Applied Anatomy for Students and Junior Doctors
الجزء والصفحة:
13th Edition , p20-23
2025-02-20
1371
The trachea (Fig1 , 2 ) is approximately 4.5 in (11.5 cm) in length and nearly 1 in (2.5 cm) in diameter. It commences at the lower border of the cricoid car tilage (C6) and terminates by bifurcating at the level of the sternal angle of Louis (T4/5) to form the right and left main bronchi. (In the living subject, the level of bifurcation varies slightly with the phase of respiration; in deep inspiration it descends to T6 and in expiration it rises to T4.)
Relations
Lying partly in the neck and partly in the thorax (superior mediastinum), its relations are as follows.
Cervical
• Anteriorly – the isthmus of the thyroid gland, inferior thyroid veins, sternohyoid and sternothyroid muscles.
• Laterally – the lobes of the thyroid gland and the common carotid artery.
• Posteriorly – the oesophagus with the recurrent laryngeal nerve lying in the groove between the oesophagus and trachea (Fig. 3).
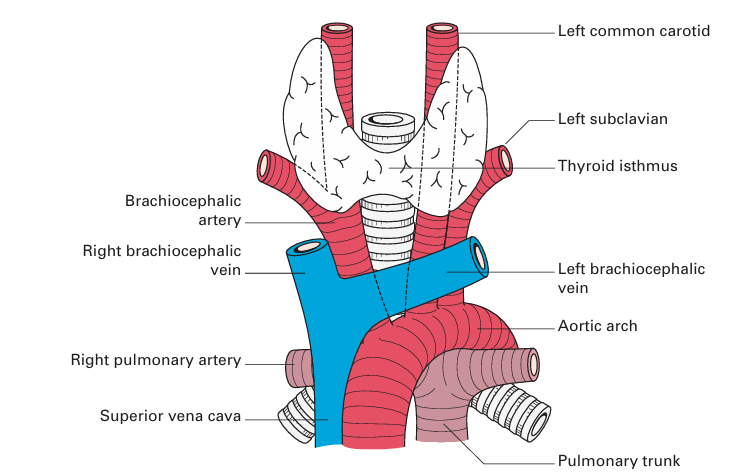
Fig1. The trachea and its anterior relationships.
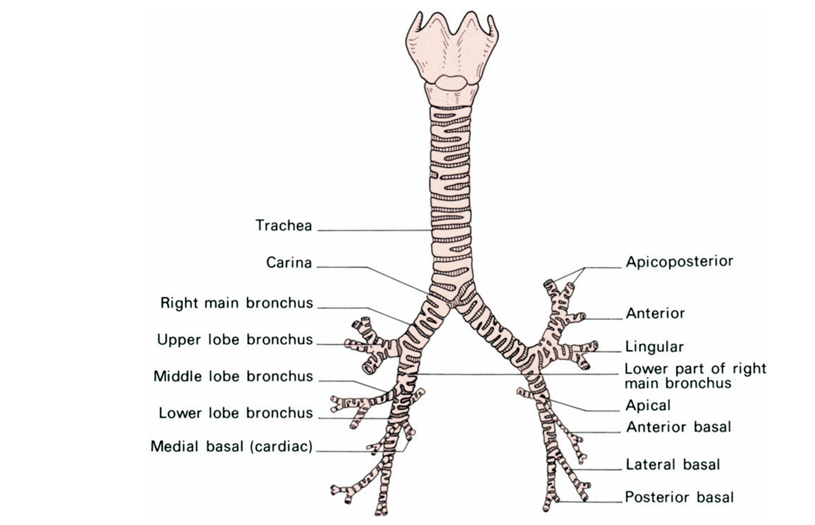
Fig2. The trachea and main bronchi viewed from the front.
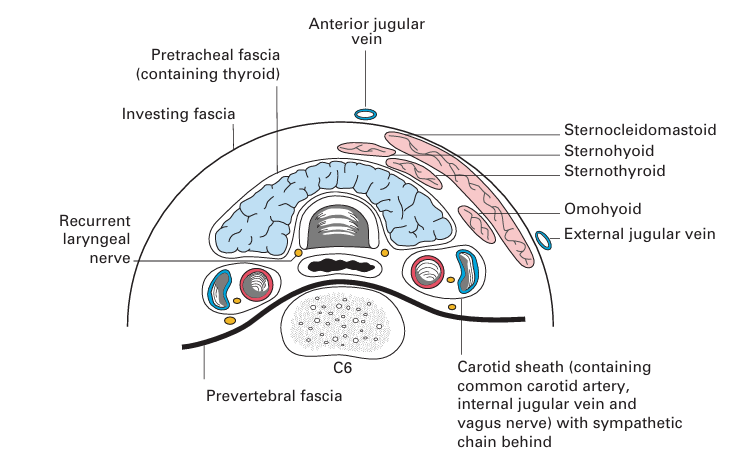
Fig3. The cervical part of the trachea and its environs in transverse section (through the 6th cervical vertebra) (viewed from below).
Thoracic
• Anteriorly – commencement of the brachiocephalic artery and left carotid artery, both arising from the arch of the aorta, the left brachio cephalic vein and the thymus.
• Posteriorly – oesophagus and left recurrent laryngeal nerve.
• To the left – arch of the aorta, left common carotid and left subclavian arteries, left recurrent laryngeal nerve and pleura.
• To the right – vagus, azygos vein and pleura (Fig. 4).
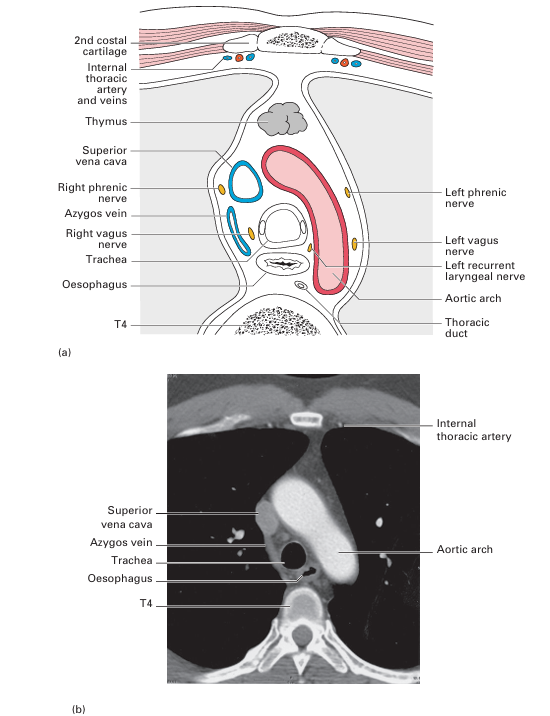
Fig4. (a) The thoracic part of the trachea and its environs in transverse section (through the 4th thoracic vertebra) (viewed from below). (b) CT scan (axial view) of the superior mediastinum at a level corresponding to that in (a).
Structure The patency of the trachea is maintained by a series of 15–20 U-shaped cartilages. Posteriorly, where the cartilage is deficient, the trachea is flattened and its wall completed by fibrous tissue and a sheet of smooth muscle (the trachealis). Within, it is lined by a ciliated columnar epithelium with many goblet cells.
 الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















