

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
The ribs
المؤلف:
Harold Ellis,Vishy Mahadevan
المصدر:
Clinical Anatomy Applied Anatomy for Students and Junior Doctors
الجزء والصفحة:
13th Edition , p8-9
2025-02-05
1795
The greater part of the thoracic cage is formed by the twelve pairs of ribs. Of these, the first seven (the ‘true ribs’) are connected anteriorly by way of their costal cartilages to the sternum, the cartilages of the 8th, 9th and 10th articulate each with the cartilage of the rib above (‘false ribs’) and the last two ribs are free anteriorly (‘floating ribs’).
Each typical rib (Fig. 1) has a head bearing two articular facets, for articulation with the upper demifacet on the side of the body of the numerically corresponding thoracic vertebra and the lower demifacet of the vertebra above . Thus, the head of the third rib articulates with its own third vertebral body and the one above. The head continues as a stout neck, which gives attachment to the costotransverse ligaments, a tubercle with a rough non-articular portion and a smooth facet, for articulation with the transverse process of the corresponding vertebra, and a long shaft flattened from side to side and divided into two parts by the ‘angle’ of the rib. The angle demarcates the lateral limit of attachment of the erector spinae muscle.
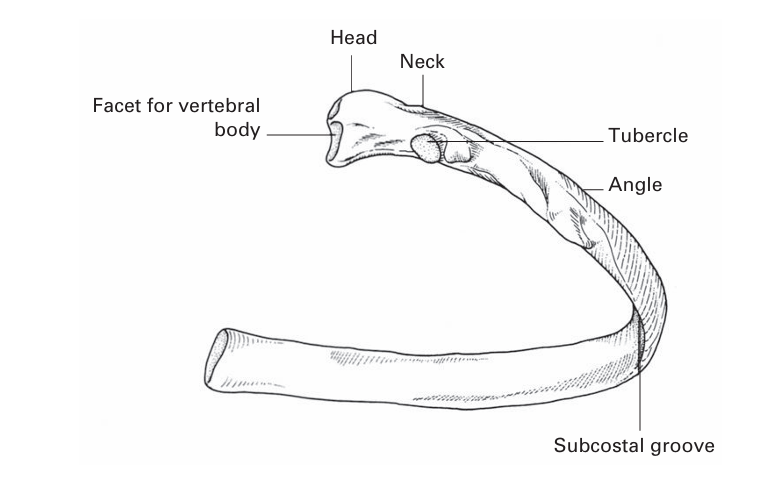
FIG1. A typical rib.
The following are the significant features of the ‘atypical’ ribs. The 1st rib (Fig. 2) is flattened from above downwards. It is not only the flattest but also the shortest and most highly curved of all the ribs. It has a prominent tubercle on the inner border of its upper surface for the insertion of scalenus anterior. In front of this tubercle, the subclavian vein crosses the rib; behind the tubercle is the subclavian groove, where the subclavian artery and lowest trunk of the brachial plexus lie in relation to the bone. This is one of the sites where the anaesthetist can infiltrate the plexus with local anaesthetic.

FIG2. Structures crossing the first rib.
Crossing the front of the neck of the first rib from the medial to the lateral side are the sympathetic trunk, the superior intercostal artery (from the costocervical trunk) and the large branch of the first thoracic nerve to the brachial plexus.
The 2nd rib is much less curved than the 1st and approximately twice as long.
The 10th rib has only one articular facet on the head. The 11th and 12th ribs (the ‘floating ribs’) are short, have no tubercles and only a single facet on the head. The 11th rib has a slight angle and a shallow subcostal groove; the 12th has neither of these features.
 الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















