


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 29-9-2017
Date: 5-10-2020
Date: 20-9-2017
|
PHENOL-FORMALDEHYDE RESINS
Phenol-formaldehyde resins are the oldest thermosetting polymers.
They are produced by a condensation reaction between phenol and formaldehyde. Although many attempts were made to use the product and control the conditions for the acid-catalyzed reaction described by Bayer in 1872, there was no commercial production of the resin until the exhaustive work by Baekeland was published in 1909. In this paper, he deseribes the product as far superior to amber for pipe stem and similar articles, less flexible but more durable than celluloid, odorless, and fire-resistant.
The reaction between phenol and formaldehyde is either base or acid catalyzed, and the polymers are termed resols (for the base catalyzed) and novalacs (for the acid catalyzed). The first step in the base-catalyzed reaction is an attack by the phenoxide ion on the carbonyl carbon of formaldehyde, giving a mixture of ortho- and para-substituted mono-methylolphenol plus di- and trisubstituted methylol phenols:
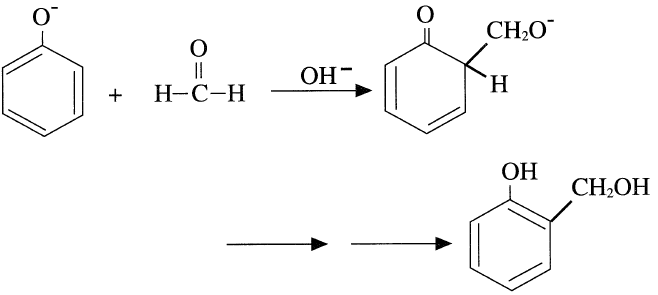
The second step is the condensation reaction between the methylolphenols with the elimination of water and the formation of the polymer.
Crosslinking occurs by a reaction between the methylol groups and results in the formation of ether bridges. It occurs also by the reaction of the methylol groups and the aromatic ring, which forms methylene bridges. The formed polymer is a three-dimensional network thermoset:

The acid-catalyzed reaction occurs by an electrophilic substitution where formaldehyde is the electrophile. Condensation between the methylol groups and the benzene rings results in the formation of methylene bridges. Usually, the ratio of formaldehyde to phenol is kept less than unity to produce a linear fusible polymer in the first stage.
Crosslinking of the formed polymer can occur by adding more formaldehyde and a small amount of hexamethylene tetramine (hexamine, (CH2)6N4). Hexamine decomposes in the presence of traces of moisture to formaldehyde and ammonia. This results in crosslinking and formation of a thermoset resin:
 .
.



|
|
|
|
لخفض ضغط الدم.. دراسة تحدد "تمارين مهمة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
طال انتظارها.. ميزة جديدة من "واتساب" تعزز الخصوصية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
عوائل الشهداء: العتبة العباسية المقدسة سبّاقة في استذكار شهداء العراق عبر فعالياتها وأنشطتها المختلفة
|
|
|