


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 19-10-2016
Date: 30-10-2016
Date: 18-10-2016
|
Concepts of Growth and Division of The Cell
The life cycle of individual organisms includes the stages of initiation, growth, and death. Individual cells also have a life cycle, the cell cycle. Cells are initiated by division of a mother cell, grow for a period, and usually cease to exist by dividing and producing two daughter cells (Fig. 1). This is not a real death because the substance of the mother cell continues to exist in the daughter cells.
As a multicellular organism grows, this type of cell cycle is common (about 25 million cell divisions occur every second in your own body). But as parts of a plant reach their final form, most cells stop dividing (cell cycle arrest) and enter an extended period of growth, during which they differentiate and mature. For example, leaf cells stop dividing when the leaf is only a few millimeters long; they continue to grow as the leaf expands and then function for the rest of the leaf's life. Leaf cells cannot normally be stimulated to begin dividing again; if the leaf is damaged, very little regeneration is possible. In contrast, cortex cells in the stem or root also stop dividing before the organ is mature, but if damage occurs the remaining cells resume division and remain active until the damaged portion has been sealed off with a layer of protective cork.

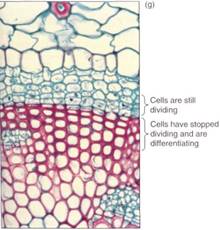
FIGURE 1: The cell cycle consists of division and growth phases. (a) The cell has grown and is ready for division; (b) first the nucleus divides, (c) then the cytoplasm is divided by the formation of a new wall. (d) The new cells enter a new cell cycle by growing. (e) Then one divides again, but the other may begin to differentiate; in this example its wall (red) thickens as it matures into a fiber. (f) The upper cell has finished dividing, and both may enter new cell cycles. The lower cell continues differentiation; in some fiber cells the nucleus may divide once or twice, but usually once fiber differentiation begins, the nucleus never divides again. (g) A cross-section of a set of cells similar to those depicted in (a) to (f); the red cells have stopped dividing and are differentiating into fiber cells. The blue cells with thin walls are still capable of growth and cell division (X 250).
Some cells live for many years, even hundreds of years, but others die shortly after they mature. Bark cells are more protective if they are dead (Fig. 2); many flower parts die only a few days after the flower first opens; and gland cells often die after a brief period of secretion.
Some cells never stop dividing. Cells in the growing points at the tips of roots and shoots are constantly cycling (Fig. 3), as are those that form wood and bark (the cambium). When a cambial cell divides, one of the new daughters becomes a wood or bark cell and the other remains part of the dividing layer. The wood or bark cell divides a low times, then differentiates, matures, and usually does not divide again. The daughter cell that stays in the dividing layer grows back to its original size and divides again. The cell cycle can be divided into a growth phase and a division phase.
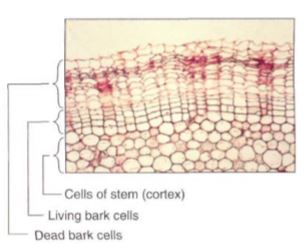
FIGURE 2 : Cells in this geranium bark divide only a few times, then differentiate by placing antimicrobial compounds in their walls along with waterproofing compounds. The cells then die and degenerate to cell walls without protoplasts. The lack of a protoplast is selectively advantageous because if a fungus or insect does penetrate the wall, it encounters no nutritious protoplasm and starves .

FIGURE 3 :The growing shoot tip of a cactus (Cleistocactus). All its cells are alive and undergo repeated cell division. One of the basic roles of shoot tips is to convert nutrients into new cells that can later differentiate into shoot tissues. At the base, cells are lightly stained because their large vacuoles do not absorb the stain; these cells cycle more slowly than the smaller, less vacuolate cells at the tip (X 80).



|
|
|
|
اكتشاف تأثير صحي مزدوج لتلوث الهواء على البالغين في منتصف العمر
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
زهور برية شائعة لتر ميم الأعصاب التالفة
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تنظم مجلس عزاء بذكرى شهادة الإمام جعفر الصادق (عليه السلام)
|
|
|
|
الأمانة العامة للعتبة الكاظمية المقدسة .. تُجري قرعة الحج ضمن حصتها المقرّرة لخدّام الإمامين الكاظمين "عليهما السلام"
|
|
|
|
مواكب كربلاء الشهادة توافدت إلى أرض الكاظمين لتعزي بشهادة صادق الأئمة "عليه السلام"
|
|
|
|
مواكب مدينة القاسم "عليه السلام" تُفصح عن مشاعرها وولاءها وهي تحيي شهادة الإمام الصادق "عليه السلام"
|