


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 25-7-2016
Date: 22-8-2016
Date: 6-9-2016
|
Radiation of Accelerating Positron
A nonrelativistic positron of charge e and velocity v1 (v1 << c) impinges head-on on a fixed nucleus of charge Ze (see Figure 1.1). The positron, which is coming from far away (∞), is decelerated until it comes to rest and then is accelerated again in the opposite direction until it reaches a terminal velocity v2. Taking radiation loss into account (but assuming it is small), find v2 as a function of v1 and Z.

Figure 1.1
SOLUTION
In first approximation, we disregard the radiation loss, i.e., we consider the energy to be constant at any given moment:
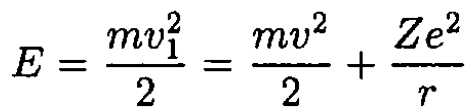 (1)
(1)
From this equation, we may find as a function of r (t) and then calculate
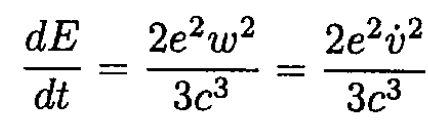 (2)
(2)
where ω is the acceleration of the positron. We should check at the end that the energy change due to radiation is small compared to the initial energy. From (1)
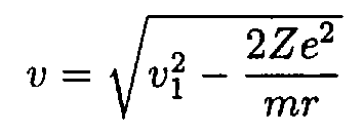 (3)
(3)
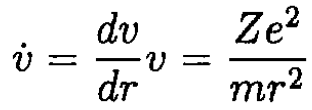 (4)
(4)
Substituting (4) into (2) and integrating, we have
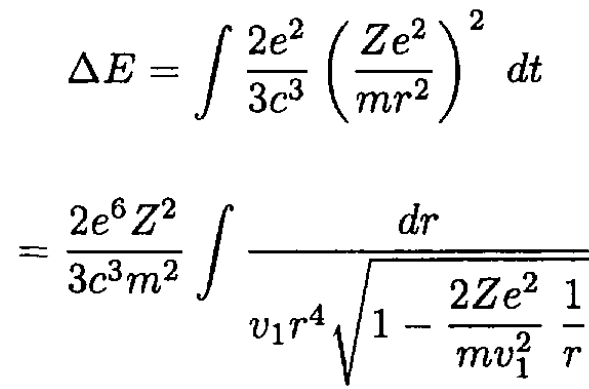 (5)
(5)
We should integrate (5) from ∞ to rmin and then from rmin to ∞, again only when ∆E << E0. In our approximation, we can say that the radiation during the deceleration is the same as for the period of acceleration and simply write
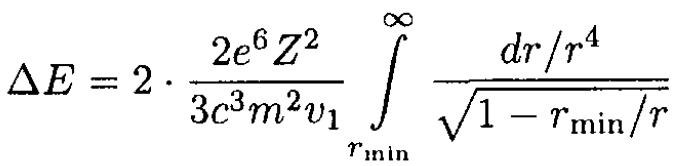 (6)
(6)
where 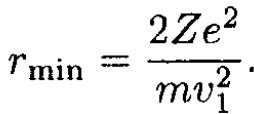 Substituting η ≡ rmin/r (6) becomes
Substituting η ≡ rmin/r (6) becomes
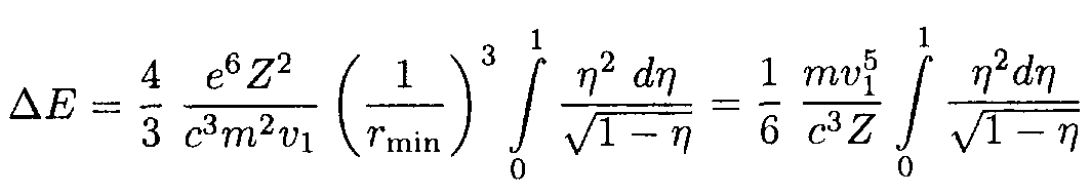 (7)
(7)
Integrating by parts,
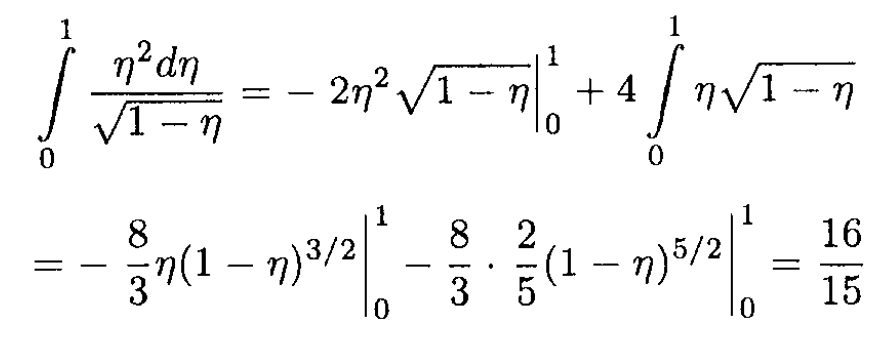
Therefore,
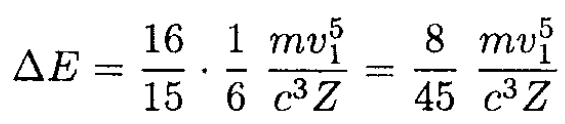
Check our initial assumption:
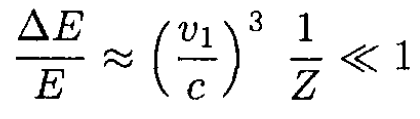
So
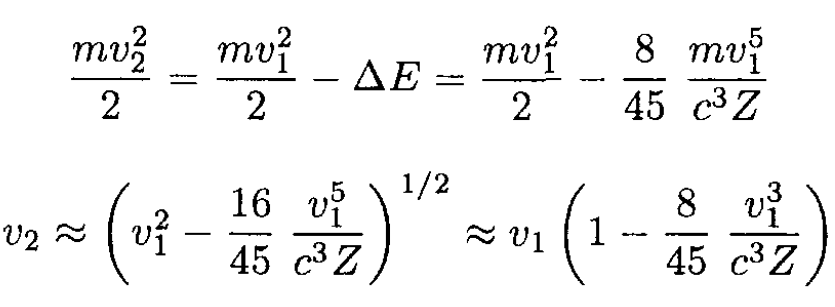



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تستعد لإطلاق الحفل المركزي لتخرج طلبة الجامعات العراقية
|
|
|