


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 30-8-2016
Date: 28-7-2016
Date: 18-8-2016
|
Electron–Electron Collision
An electron of total energy 1.40 MeV collides with another electron which is at rest in the laboratory frame. Let the electronic rest energy be 0.51 MeV.
a) What are the total energy and momentum of the system in the laboratory frame of reference (specify momentum in Mev/c units)?
b) Find the velocity of the center of mass in the laboratory frame.
c) Determine the total energy of the pair of particles in the center of mass frame of reference (CMF).
d) The target electron scatters at an angle of 45° in the CMF. What will be the direction of scatter of the projectile in the CMF? What will be the energy and momentum of the target electron after scatter in the CMF?
e) What, in the laboratory frame, will be the target electron’s momentum components perpendicular and parallel to the direction of the incoming particle after the collision?
SOLUTION
a) The total energy in the laboratory frame
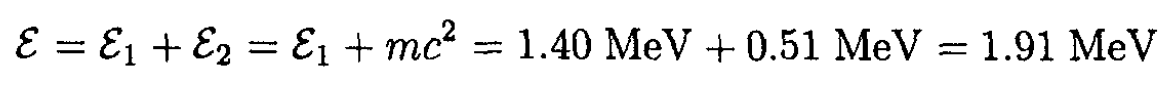
where ε1 is the energy of the moving electron and ε2 = mc2 is the energy of the electron at rest. The total momentum is simply the momentum p1 of the moving electron
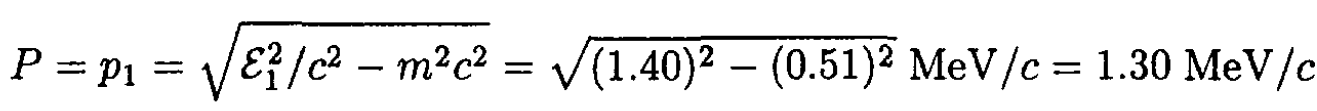
b) The velocity of the center of mass in the lab frame is defined as
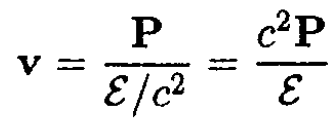
where P and ε are the total momentum and energy in the lab frame, respectively.
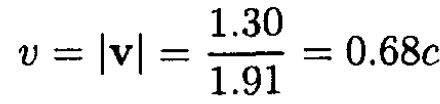
c) The total energy in the CMF ε' (P' = 0) is given by
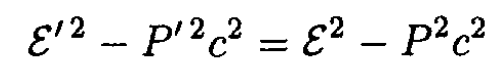
so
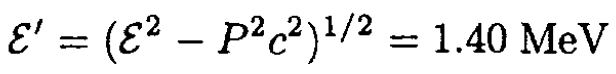
We may also calculate the total energy in the CMF by transforming the energy of the target from the laboratory frame to the CMF:
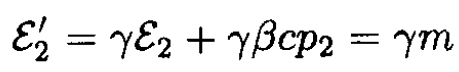
Since the target and the projectile have the same energy in the CMF, the total energy is given by
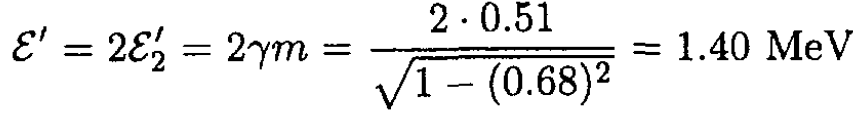
d) In the center of mass frame the total momentum P = 0, therefore, p1 = -p2 and the angle of the scatter α = 135o. The momentum can be found by considering the 4-momentum of the two particles. We will use another method here. Before the collision the projectile had a momentum p1 in the lab frame; in the CMF it had a momentum
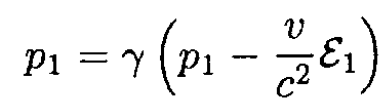
p1 and p'2 are both along the  axis
axis
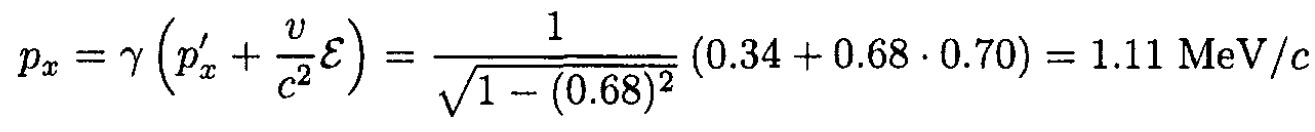
As a result of the collision, the momentum of the projectile will only rotate, and the momentum of the target
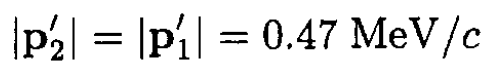
The energy of the target 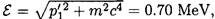 or from the same transformation as that of the projectile
or from the same transformation as that of the projectile
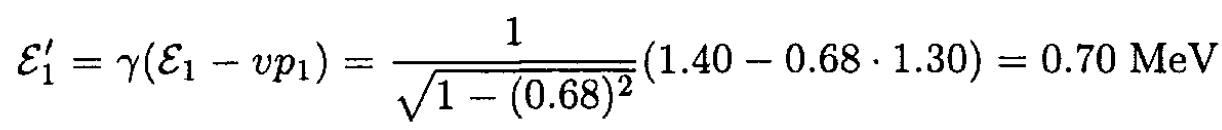
which is, of course, the same as above, where we used the fact that the energy of the projectile is equal to the target energy, since the masses of the two particles are the same.
e) In the ŷ direction perpendicular to the direction of the incoming particle
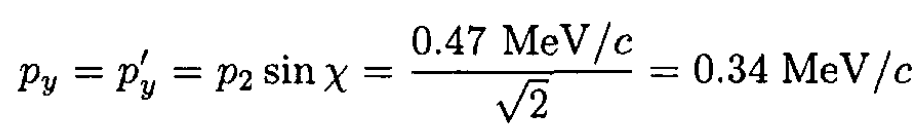
To find the  component in the lab frame we can again use the Lorentz transformation of momentum
component in the lab frame we can again use the Lorentz transformation of momentum
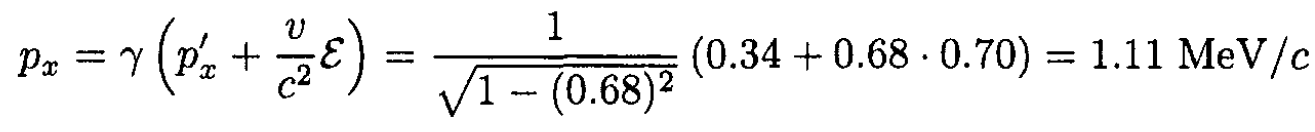 .
.



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ضمن أسبوع الإرشاد النفسي.. جامعة العميد تُقيم أنشطةً ثقافية وتطويرية لطلبتها
|
|
|