


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 30-3-2016
Date: 27-3-2016
Date: 30-3-2016
|
Fluoroquinolones
Agents: ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, gemifloxacin
Many of the fluoroquinolones are near-ideal antibiotics: they have broad-spectrum activity that includes Gram-positive, Gram-negative, and atypical organisms; display excellent oral bioavailability; and have a relatively low incidence of adverse effects. Unfortunately, these characteristics have led to overprescribing and the inevitable rise in resistance, despite recommendations to reserve this class. In particular, although activity against enteric Gram-negative organisms (such as E. coli and Klebsiella) has historically been excellent, in certain geographical regions or patient populations these drugs have lost much of their potency. The newer drugs (moxifloxacin, gemifloxacin) gain in-creasing Gram-positive (mostly pneumococcal) activity at the expense of some Gram-negative (mostly Pseudomonas) activity. Significant differences among the agents are in bold.
Spectrum: Ciprofloxacin
Good: enteric GNRs (E. coli, Proteus, Klebsiella,
etc.), H. influenzae
Moderate: Pseudomonas, atypicals (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, Legionella)
Poor : staphylococci, S. pneumoniae, anaerobes, enterococci
Spectrum: Levofloxacin/Moxifloxacin/Gemifloxacin
Good: enteric Gram negatives, S. pneumoniae, atypicals, H. influenzae
Moderate: Pseudomonas (levofloxacin only), MSSA
Poor : anaerobes (except moxifloxacin, which has moderate activity), enterococci
Adverse Effects
GI side effects, headache, and photosensitivity are most common. Rare but serious side effects usually occur in patients with underlying conditions: hyper-or hypoglycemia (diabetes), seizures (seizure disorder), prolongation of the QT interval (underlying arrhythmia or proarrhythmic medications). These effects are dose related, so carefully review dosing in patients with renal dysfunction and the elderly. Arthralgias (uncommonly) and Achilles tendon rupture (very rarely) may occur. Fluoroquinolones also can cause CNS adverse reactions, including dizziness, confusion, and hallucinations. Elderly patients are particularly susceptible to these. Younger patients may develop insomnia.
Because of toxicities seen in juvenile beagle dogs, fluoroquinolones are absolutely contraindicated in pregnant women and relatively contraindicated in children, although experience with use in children suggests they may be used safely.
Dosing Issues
While ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin have activity against Pseudomonas, MICs are typically higher than with other susceptible organisms (e.g., E. coli). Thus, when using these drugs to treat documented or possible Pseudomonas infections, give them at higher, antipseudomonal doses: 400 mg IV q8h or 750 mg PO q12h for ciprofloxacin; 750 mg IV/PO daily for levofloxacin.
Important Facts
• Bioavailability of all fluoroquinolones is 80–100%, so oral dose = IV dose (except ciprofloxacin: PO = 1.25 times IV dose).
• Fluoroquinolones chelate cations, and their oral bioavailability is significantly decreased when administered with calcium, iron, antacids, milk, or multivitamins. Separate these agents by at least 2 hours or have your patient take a week off of the supplements, if possible. Administration with tube feedings is also problematic. This problem is unique to the oral formulations—IV forms avoid it.
• Most fluoroquinolones are cleared renally and require dose reduction in renal dysfunction. Moxifloxacin is the exception; because it is not excreted into the urine, it is also not approved for treatment of UTIs. Gemifloxacin has dual elimination, and its utility in treating UTIs is not yet established, though it does require dose adjustment in renal failure. It is probably best to avoid using gemifloxacin for UTIs until there is evidence that supports its use.
• The FDA has recently added a black box warning to all fluoroquinolone package inserts regarding the possibility of tendon rupture.
What They’re Good For
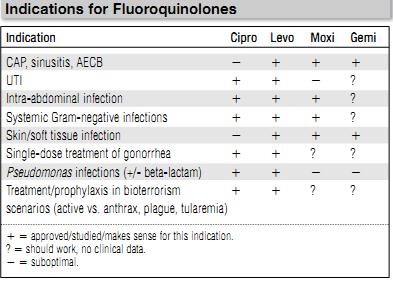
Not everything, despite the temptation. Remember, the longer you want to be able to use these drugs, the more restraint should be exercised now. Indications for the fluoroquinolones are listed in table 1.
Don’t Forget!
When using the oral forms of fluoroquinolones, be especially careful to avoid co-administering with chelating agents (calcium, magnesium, aluminum, etc.). Also be cautious of using these drugs in patients with conditions or drugs that prolong the QT interval.
Table 1
References
Gallagher ,J.C. and MacDougall ,c. (2012). Antibiotics Simplified. Second Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC.



|
|
|
|
مخاطر عدم علاج ارتفاع ضغط الدم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
البحرين تفوز بجائزة أفضل وجهة للمعارض والمؤتمرات
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مدرسة دار العلم.. صرح علميّ متميز في كربلاء لنشر علوم أهل البيت (عليهم السلام)
|
|
|