


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 2025-03-20
Date: 2025-03-26
Date: 2025-03-30
|
(Androstenediones [AD], Dehydroepiandrosterone [DHEA], Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate [DHEA S], 11-Deoxycortisol, 17 Hydroxyprogesterone, 17-Hydroxypregnenolone, Pregnenolone)
Type of test Blood
Normal findings
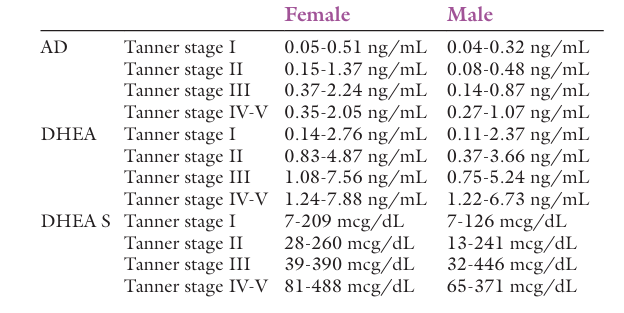
Test explanation and related physiology
Androstenediones (ADs, DHEA, and the sulfuric ester, DHEA S) are precursors of testosterone and estrone and are made in the gonads and the adrenal gland. 11- Deoxycortisol, 17- hydroxyprogesterone, 17-hydroxypregnenolone, and pregnenolone are precursors of cortisol. ACTH stimulates their adrenal secretion. Children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) have genetic mutations that cause deficiencies in the enzymes involved in the synthesis of cortisol, testosterone, aldosterone, and estrone. When defects in enzyme synthesis occur along the path of hormone synthesis, the previously listed precursors exist in levels that exceed normal through the increased stimulation of ACTH.
The symptoms of the disorder depend on which steroids are overproduced and which are deficient. As a result, CAH may present with various symptoms, including virilization of the affected female infant, signs of androgen excess in males and females, signs of sex hormone deficiency in males and females, salt-wasting crisis secondary to cortisol and aldosterone deficiency, or hormonal hypertension due to increased mineralocorticoids. A milder, nonclassic form of CAH is characterized by premature puberty, acne, hirsutism, menstrual irregularity, and infertility .
These same precursors can occur in adults due to adrenal or gonadal tumors. Patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (Stein Leventhal syndrome) have particularly elevated levels of ADs. DHEA S levels are particularly high in patients with adrenal carcinoma.
In patients suspected of CAH, testing for a panel of steroids involved in the cortisol biosynthesis pathway may be performed to establish the specific enzyme deficiency. In most cases, basal concentrations within the normal reference interval rule out CAH. The ratio of the precursor to the final pathway product (with and without ACTH stimulation) may be used to diagnose which enzyme is deficient.
Interfering factors
• A radioactive scan performed 1 week before the test may invalidate the test results if radioimmunoassay is performed.
* Drugs that may increase levels of ADs include clomiphene, corticotropin, and metyrapone.
* Drugs that may decrease levels of ADs include steroids.
Procedure and patient care
• See inside front cover for Routine Blood Testing.
• Fasting: no •
Blood tube commonly used: serum separator or red
* Tell the female patient that the specimen should be collected 1 week before or after the menstrual period.
• Indicate the date of the last menstrual period (if applicable) on the laboratory form.
Abnormal findings
Increased levels
- Adrenal tumor
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Ectopic ACTH-producing tumors
- Cushing syndrome (some cases)
- Stein-Leventhal syndrome
- Ovarian sex cord tumor
Decreased levels
- Gonadal failure
- Primary or secondary adrenal insufficiency



|
|
|
|
حقن الذهب في العين.. تقنية جديدة للحفاظ على البصر ؟!
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"عراب الذكاء الاصطناعي" يثير القلق برؤيته حول سيطرة التكنولوجيا على البشرية ؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جمعية العميد تعقد اجتماعها الأسبوعي لمناقشة مشاريعها البحثية والعلمية المستقبلية
|
|
|