
 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
أقرأ أيضاً
التاريخ: 13-8-2021
التاريخ: 6-9-2017
التاريخ: 22-11-2018
التاريخ: 24-11-2015
|
All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model, which is subsequently replaced by bone. This kind of ossification is called endochondral ossification; and bones formed in this way are called cartilage bones. In some situations (e.g., the vault of the skull) formation of bone is not preceded by formation of a cartilaginous model. Instead bone is laid down directly in a fibrous membrane. This process is called intramembranous ossification; and bones formed in this way are called membrane bones. T he bones of the vault of the skull, the mandible, and the clavicle are membrane bones.
intramembranous ossification
The various stages in intramembranous ossification are as follows:
- At the site where a membrane bone is to be formed the mesenchymal cells become densely packed (i.e., a mesenchymal condensation is formed).
- The region becomes highly vascular.
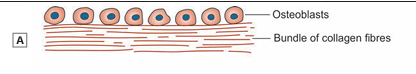
- Some of the mesenchymal cells lay down bundles of collagen fibres in the mesenchymal condensation. In this way a membrane is formed.
- Some mesenchymal cells (possibly those that had earlier laid down the collagen fibres) enlarge and acquire a basophilic cytoplasm, and may now be called osteoblasts (Fig)
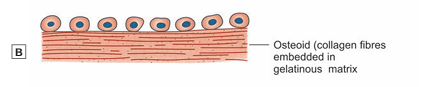
They come to lie along the bundles of collagen fibres. These cells secrete a gelatinous matrix in which the fibres get embedded. The fibres also swell up. Hence the fibres can no longer be seen distinctly. This mass of swollen fibres and matrix is called osteoid (Fig)
- Under the influence of osteoblasts calcium salts are deposited in osteoid. As soon as this happens the layer of osteoid can be said to have become one lamellus of bone (Fig. )
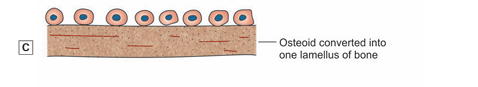
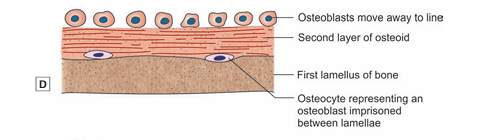
- Over this lamellus, another layer of osteoid is laid down by osteoblasts. The osteoblasts move away from the lamellus to line the new layer of osteoid. However, some of them get caught between the lamellus and the osteoid (Fig).
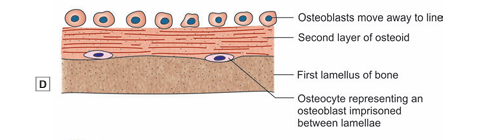
The osteoid is now ossified to form another lamellus. The cells trapped between the two lamellae become osteocytes .
- In this way a number of lamellae are laid down one over another, and these lamellae together form a trabeculus of bone (Fig).
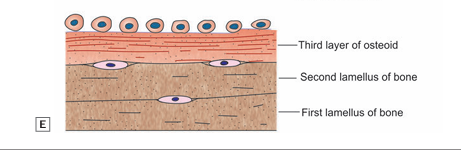
The first formed bone may not be in the form of regularly arranged lamellae. The elements are irregularly arranged and form woven bone.



|
|
|
|
هل يمكن أن تكون الطماطم مفتاح الوقاية من السرطان؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف عرائس"غريبة" عمرها 2400 عام على قمة هرم بالسلفادور
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تقيم ندوة علمية عن الاعتماد الأكاديمي في جامعة جابر بن حيّان
|
|
|