

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Types of Bone
المؤلف:
Neelam Vasudeva and Sabita Mishra
المصدر:
Inderbir Singhs Textbook of Human Histology
الجزء والصفحة:
7th edition , P93-94
2025-01-11
1233
Based on histology
- Compact bone - Spongy bone
Based on maturity
- Mature/ lamellar bone -Immature/woven bone
Based on manner of development
- Cartilage bone - Membrane bone
lamellar Bone
When we examine the structure of any bone of an adult, we find that it is made up of layers or lamellae (Fig1).
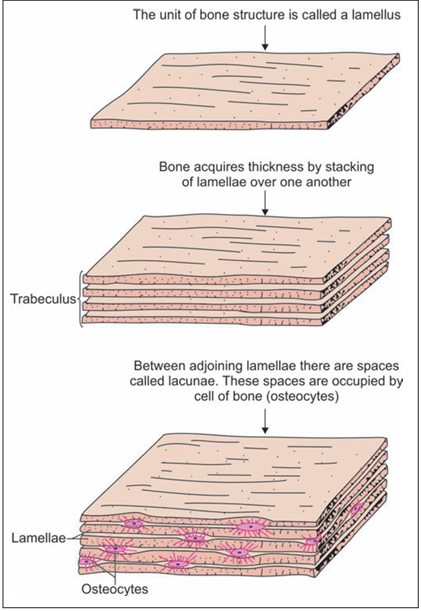
Fig 1 : How lamellae constitute bone (Schematic representation)
This kind of bone is called lamellar bone. Each lamellus is a thin plate of bone consisting of collagen fibres and mineral salts that are deposited in a gelatinous ground substance. Even the smallest piece of bone is made up of several lamellae placed over one another. Between adjoining lamellae we see small flattened spaces or lacunae. Each lacuna contains one osteocyte. Spreading out from each lacuna there are fine canals or canaliculi that communicate with those from other lacunae (Fig. 2).
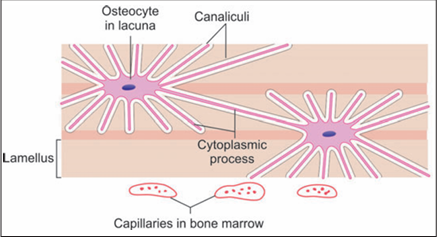
Fig 2 : Relationship of osteocytes to bone lamellae (Schematic representation)
The canaliculi are occupied by delicate cytoplasmic processes of osteocytes. The lamellar appearance (Fig. 1) of bone depends mainly on the arrangement of collagen fibres. The fibres of one lamellus run parallel to each other; but those of adjoining lamellae run at varying angles to each other. T he ground substance of a lamellus is continuous with that of adjoining lamellae .
Woven Bone
In contrast to mature bone, newly formed bone does not have a lamellar structure. The collagen fibres are present in bundles that appear to run randomly in different directions, interlacing with each other. Because of the interlacing of fibre bundles this kind of bone is called woven bone. All newly formed bone is woven bone. It is later replaced by lamellar bone.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع متنوعة أخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع متنوعة أخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















