


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 4-11-2015
Date: 4-11-2015
Date: 4-11-2015
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Electron microscopic study of sectioned cells has revealed the presence of a three dimensional network of sac-like and tubular cavities called cisternae bounded by a unit membrane inside the cell. Since these structures are concentrated in the endoplasmic portion of the cytoplasm, the entire organization is called the endoplasmic reticulum. This name was coined by Porter in 1953.
The occurrence of ER varies from cell to cell. They are absent in erythrocytes, egg cells and embryonic cells.
The ER is the site of specific enzyme controlled biochemical reactions. Its outer surface carries numerous ribosomes. The presence of ribosomes gives a granular appearance. In this condition ER is described as rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). RER is the site of synthesis of proteins. Ribosomes are absent on smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). SER is concerned with lipid metabolism.
Morphologically ER may occur in three forms namely:
1. Lamellar form
2. Vesicular form
3. Tubular form
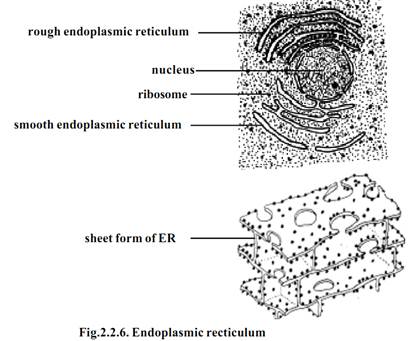
Lamellar form or Cisternae :- These are long, flat, sac like tubules. Their diameter is about 40-50 µm. The RER has a synthetic role. It is mostly seen in cells of pancreas, notochord and brain.
Vesicles :- These are oval, vacuolar structures. Their diameter is about 25-500 µm. They occur in most of the cells.
Tubules: - These are branched structures forming the reticular system along with the cisternae and vesicles. They have a diameter of 50-190 µm. They occur in almost all cells.
Functions:
1-It provides skeletal framework to the cell
2-It facilitates exchange of molecules by the process of osmosis, diffusion and active transport
3-Enzymes of ER control several metabolic activities
4-They serve as intracellular transporting system
5-It conducts intra-cellular impulses
6-It helps to form nuclear membrane after cell division
7-SER synthesises lipids
References
T. Sargunam Stephen, Biology (Zoology). First Edition – 2005, Government of Tamilnadu.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مدرسة دار العلم.. صرح علميّ متميز في كربلاء لنشر علوم أهل البيت (عليهم السلام)
|
|
|