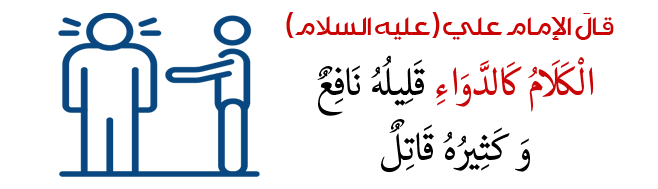


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2023-10-31
Date: 2023-11-25
Date: 26/11/2022
|
One more technical term and one last fact about heads and complements. The relationships between heads and modifiers are called dependencies or dependency relations. heads have been described as controlling modifiers; modifiers are said to depend on, or to be dependent on, their heads. Heads and their modifiers typically cluster together to form a phrase, certainly in formal written language. In accordance with a long tradition in Europe, verbs are treated here as the head, not just of phrases, but of whole clauses. In clauses, the verb and its complements tend to occur close together, with the adjuncts pushed towards the outside of the clause, as shown by the examples in (9). (Remember that the subject noun is regarded as a complement, since it is obligatory.)
 In (9a), the object her car is next to the verb, followed by the directional phrases from Morningside and to Leith. As discussed above, objects and directional phrases are complements. The time-when phrase on Wednesday is at the end of the clause in (9a) and at the beginning of the clause in (9b). In (9b), it is closer to drove, but this is not important. What is important is the fact that the adjunct does not come between the head and any of the complements. This does happen in (9c), where on Wednesday separates the complement her car from the other complement to Leith. Example (9c) is at the least awkward – although there might be contexts in which that order of phrases would be appropriate.
In (9a), the object her car is next to the verb, followed by the directional phrases from Morningside and to Leith. As discussed above, objects and directional phrases are complements. The time-when phrase on Wednesday is at the end of the clause in (9a) and at the beginning of the clause in (9b). In (9b), it is closer to drove, but this is not important. What is important is the fact that the adjunct does not come between the head and any of the complements. This does happen in (9c), where on Wednesday separates the complement her car from the other complement to Leith. Example (9c) is at the least awkward – although there might be contexts in which that order of phrases would be appropriate.
|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ندوات وأنشطة قرآنية مختلفة يقيمها المجمَع العلمي في محافظتي النجف وكربلاء
|
|
|