


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 7-12-2021
Date: 14-11-2021
Date: 6-9-2021
|
DNA Cloning : Sequencing cloned DNA fragments
The base sequence of DNA fragments that have been cloned can be determined. The original procedure for this purpose was the Sanger dideoxy chain termination method illustrated in Figure 1. In this method, the single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) to be sequenced is used as the template for DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase (DNA pol). A radiolabeled primer complementary to the 3′-end of the target DNA is added, along with the four deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (dNTP). The sample is divided into four reaction tubes, and a small amount of one of the four dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (ddNTP) is added to each tube.
Because it contains no 3′-hydroxyl group, incorporation of a ddNMP terminates elongation at that point. The products of this reaction, then, consist of a mixture of DNA strands of different lengths, each terminating at a specific base. Separation of the various DNA products by size in an electric field using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, followed by autoradiography, yields a pattern of bands from which the DNA base sequence can be read. [Note: The shorter the fragment, the farther it travels on the gel, with the shortest fragment representing that which was made first (that is, the 5′-end).] In place of a labeled primer, a mixture of the four ddNTP linked to different fluorescent dyes and in a single reaction tube is now commonly used. The mixture is separated by capillary electrophoresis, the fluorescent labels are detected, and a color readout of the sequence is generated (Fig. 2). [Note: The Human Genome Project used variations of this technique to sequence the human genome.] Advances in sequencing technology, so-called next generation, or high-throughput sequencing, now allow the rapid sequencing of an entire genome with increased fidelity and decreased cost through the simultaneous (parallel) sequencing of many DNA pieces. [Note: Sequencing of the exome, that portion of the genome that encodes proteins, is now possible.]
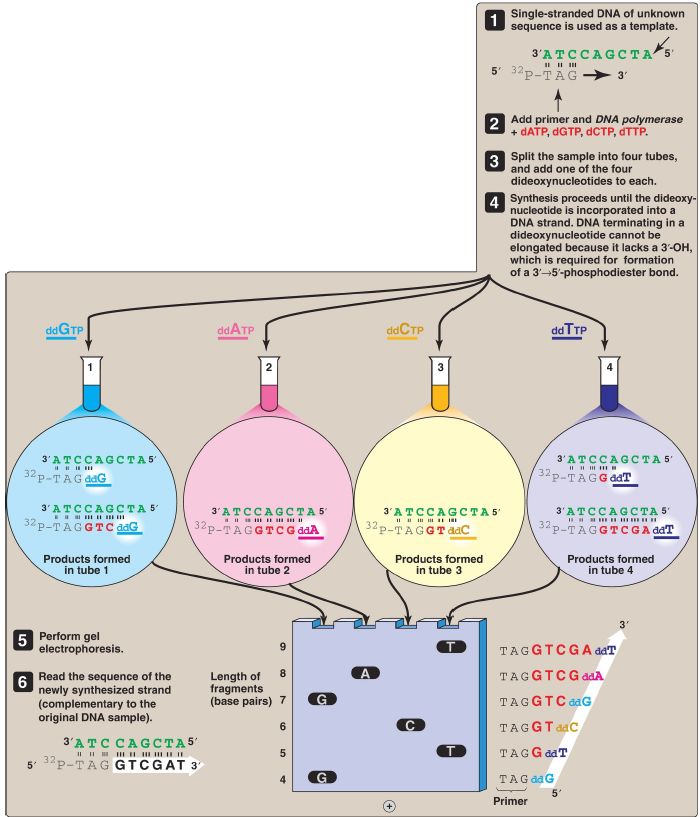
Figure 1: DNA sequencing by the Sanger dideoxy method. [Note: The original method utilized a radiolabeled primer. Fluorescent dye-labeled dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates are now commonly used.] A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; d = deoxy; dd = dideoxy.

Figure 2: Color readout of a DNA sequence.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|