


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 3-5-2021
Date: 11-4-2021
Date: 5-5-2021
|
Basic FET amplifier circuit
In Fig. 1, an N-channel JFET is hooked up as a common-source amplifier. The input signal passes through C2 to the gate. Resistor R2 provides the bias. Resistor R1 and capacitor C1 give the source a dc voltage relative to ground, while grounding it for ac signals. The ac output signal goes through capacitor C3. Resistor R3 keeps the ac output signal from being short-circuited through the power supply.
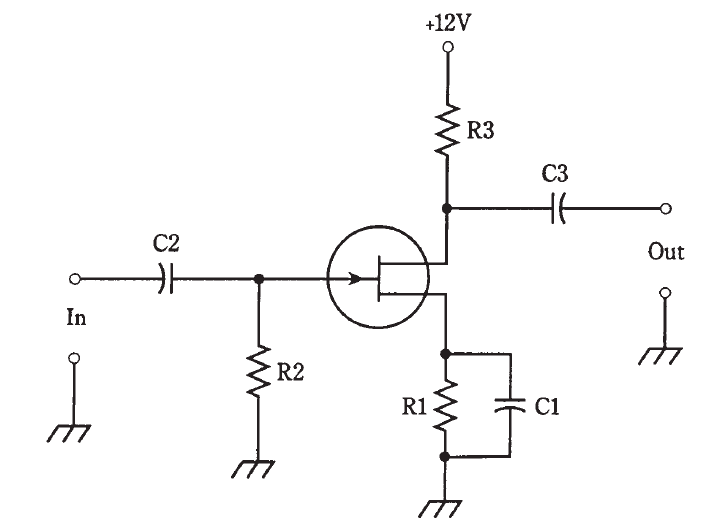
Fig. 1: An amplifier using an FET. Component designators and values are discussed in the text.
Concerning the values of the capacitors, the same considerations apply for this amplifier, as apply in the bipolar circuit. A JFET amplifier almost always has a high input impedance, and therefore the value of C2 will usually be small. If the device is a MOSFET, the input impedance is even higher, and C2 will be smaller yet, sometimes as little as 1 pF or less.
The resistor values depend on the application. In some instances, R1 and C1 are not used, and the source is grounded directly. If R1 is used, its value will depend on the input impedance and the bias needed for the FET. Nominal values might be R1 = 680 Ω, R2 = 10 KΩ, and R3 = 100 Ω for a weak-signal, wideband amplifier. If the circuit is used as a power amplifier, the values of the resistors will be different. It might be necessary to bias the gate negatively with respect to the source, using a second power supply with a voltage negative relative to ground.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مكتبة أمّ البنين النسويّة تصدر العدد 212 من مجلّة رياض الزهراء (عليها السلام)
|
|
|