


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 16-9-2020
Date: 24-5-2016
Date: 16-9-2020
|
ATOMIC NUMBER
According to modern atomic theory, every proton in the universe is exactly like every other. Neutrons are all alike too. The number of protons in an element’s nucleus, the atomic number, gives that element its identity.
The element with three protons is lithium, a light metal that reacts easily with gases such as oxygen or chlorine. Lithium always has three protons; conversely, any element with three protons in its nucleus must be lithium. The element with four protons is beryllium, also a metal. Carbon has six protons in its nucleus, nitrogen has seven, and oxygen has eight. In general, as the number of protons in an element’s nucleus increases, the number of neutrons also increases. Elements with high atomic numbers, such as lead, are therefore much more dense than elements with low atomic numbers, such as carbon. Perhaps you’ve compared a lead shot with a piece of coal of similar size and noticed this difference.
If you could somehow add two protons to the nucleus of every atom in a sample of carbon, you would end up with an equal number of atoms of oxygen. However, this is much easier said than done, even with a single atom. It is possible to change one element into another; the Sun does it all the time, fusing hydrogen into helium. The process is far from trivial, though. In ancient times, alchemists tried to do this; the most well-known example of their pursuits was the quest to turn lead (atomic number 82) into gold (atomic number 79). As far as anyone knows, they never succeeded. It was not until the 1940s, when the first atomic bombs were tested, that elements actually were “morphed” by human beings. The results were quite different from anything the alchemists ever strove for.
Table 9-1 lists all the known elements in alphabetical order, with the names of the elements in the first column, the standard chemical symbols in the second column, and the atomic numbers in the third column.
Table 1 The Chemical Elements in Alphabetical Order by Name, Including Chemical Symbols and Atomic Numbers 1 through 118 (As of the time of writing, there were no known elements with atomic numbers 113, 115, or 117.)
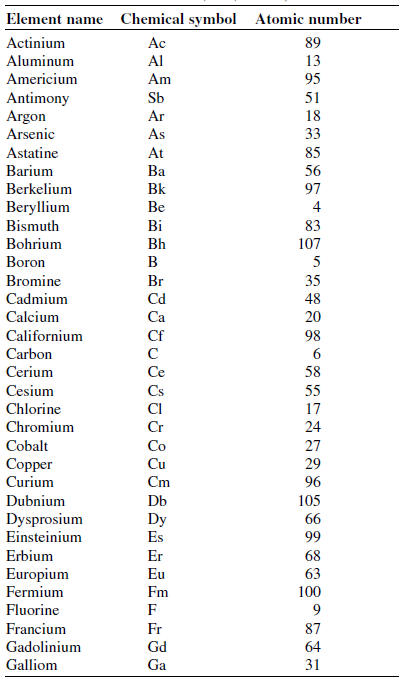



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تقدم دعوة إلى كلية مزايا الجامعة للمشاركة في حفل التخرج المركزي الخامس
|
|
|