

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Abdominal Imaging
المؤلف:
Kelly M. Harrell and Ronald Dudek
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Anatomy
الجزء والصفحة:
16-7-2021
1629
Abdominal Imaging
Interpretation of abdominal imaging requires a thorough approach. A solid understanding of the abdominal anatomy and spatial relationships is very important and useful in both plain film and computed tomography (CT) interpretation.
A. Radiology
Although a variety of radiologic approaches is possible, here we use the BBC approach, which stands for Bowel (and other organs), Bones, and Calcifications (and artifacts). Adopting a stepwise approach to interpreting radiographic images minimizes errors and maximizes the effectiveness of a treatment plan.
1. Bowel and other organs: Typically, the small bowel lies more centrally, with the large bowel framing it around the periphery (Fig. 1). You should look for mucosal fold patterns in both the small and large bowels. The small bowel folds-valvulae conniventes (plicae circularis)-span the full width of the bowel, while large bowel folds-haustral folds (plicae semilunaris)-do not completely traverse the large bowel. Normal gas patterns should also be present and outline these features. For other organs, proceed in the following order.
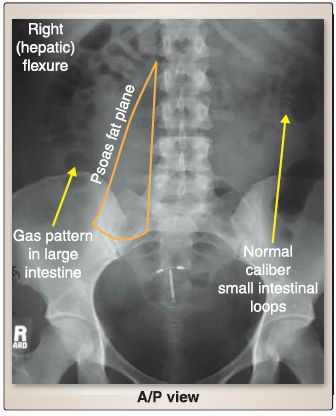
Figure 1: Plain-film radiology of the abdomen.Image shows normal bowel-gas patterns. Note dark appearance of air (gas) in large and small intestines. A/P = anterior/posterior.
a. Lungs: Check lung bases for pathology.
b. Liver: Assess size of this large right upper quadrant organ.
c. Gallbladder: This organ is difficult to see on x-ray.
d. Stomach: This left upper quadrant/midline organ may contain
variable amounts of air (gastric bubble).
e. Psoas muscles: These are located in the lumbar region. Look
for demarcation on the lateral edge (psoas fat plane).
f. Kidney: The right kidney is often more visible than the left.
g. Spleen: This left upper quadrant organ lies superior to the left
kidney. Look for enlargement.
h. Bladder: The variable size of this organ depends on fullness (in
pelvis vs. suprapubic region).
2. Bones: Use bones for important landmarks. Also look for pathology, proceeding from the ribs ➔ lumbar vertebrae, ➔ sacrum ➔ coccyx ➔ pelvis ➔ and finally to the proximal femurs.
3. Calcifications and artifacts: Various high-density areas of calcification can be visualized on an abdominal x-ray. Some examples are calcified gallstones; renal stones; pancreatic, vascular, and costochondral calcifications; and contrast. Artifacts may include surgical clips, jewelry (umbilicus), intrauterine device, and other objects. (Can you spot any of these in Fig. 3)
B. Abdominal computed tomography radiology
A solid understanding of the spatial arrangement of structures in the abdomen is essential for diagnostic and interventional radiology. A systematic approach to interpreting abdominal CT images involves identifying abdominal wall layers, peritoneal spaces/structures, normal fat planes, and solid organ location and features. Working from superficial to deep allows and left lumbar lymph nodes before sending efferents superiorly to form lumbar lymphatic trunks (right and left). These trunks, along with intestinal lymphatic trunks, join at the abdominal confluence, where a small
dilated sac-cisterna chyli-is located. Lymph then passes superiorly into the thoracic duct.
for a thorough interpretation, wherein abnormal anatomy and pathology can be identified properly. Recall that when viewing axial CT images, the patient's feet are coming out of the plane of the image and the head is into the plane. This makes the right side of the image the left side of the patient. With this in mind, organizing viscera into abdominal quadrants can help to determine position in the stacked images.
 الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















