

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Vasculature and Innervation
المؤلف:
Kelly M. Harrell and Ronald Dudek
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Anatomy
الجزء والصفحة:
10-7-2021
3060
Vasculature and Innervation
A. Vasculature
Vascular supply to the spinal cord and vertebral column originates from a number of sources (Fig. 1).
1. Arterial supply: Arterial supply to the spinal cord and vertebral column includes branches of segmental spinal arteries along the length of the cord/column.
a. Medullary arteries: The singular anterior spinal artery and paired posterior spinal arteries originate from the vertebral arteries and run the length of the spinal cord. Spinal arteries receive collateral circulation from a series of segmental medullary arteries that originate from vertebral, deep cervical, ascending cervical, posterior intercostal, lumbar, and lateral sacral arteries. The largest of these is the great anterior segmental medullary artery (artery of Adamkiewicz), which serves the lower two thirds of the spinal cord.
b. Radicular arteries: Radicular arteries supply the meningeal coverings and spinal nerve roots, but do not anastomose with spinal arteries.
c. Periosteal and equatorial branches supply arterial blood to the vertebral column (Fig. 2). Spinal branches also contribute to the bone surrounding the spinal canal. These branches arise from cervical (vertebral and ascending cervical arteries) and segmental arteries in the thoracic and lumbar regions (posterior intercostal, subcostal, lumbar, iliolumbar, and sacral arteries).
2. Venous drainage: Venous drainage of the vertebral column arises from spinal veins that originate from surrounding internal and external venous plexuses. These veins drain into segmental thoracic and lumbar veins as well as vertebral veins in the cervical
region. Venous drainage occurs through three anterior and three posterior spinal veins and a series of anterior and posterior medullary and radicular veins. These veins communicate with the internal vertebral venous plexus, which is continuous with the dural venous sinuses in the cranial vault.

Figure 1: Primary arterial blood supply of the spinal caret
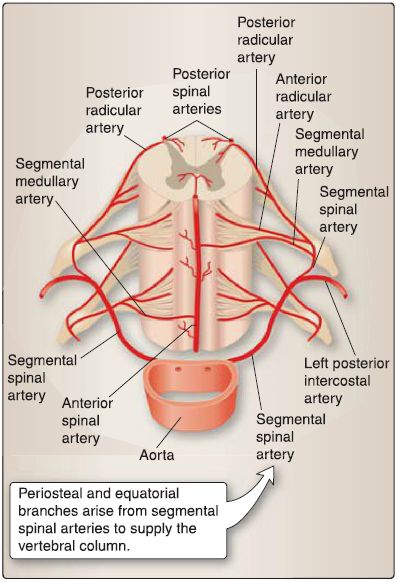
Figure 2: Cross section through spinal cord showing internal and external arterial
supply.
B. Innervation
In general, the vertebral column receives innervation from spinal nerves, specifically meningeal branches (Fig.3). These branches supply intervertebral discs, periosteum, ligaments, dura mater, and spinal blood vessels. In addition, each zygapophyseal (facet) joint is innervated by articular medial branches of posterior rami from adjacent spinal nerves, giving the synovial joint a dual innervation.
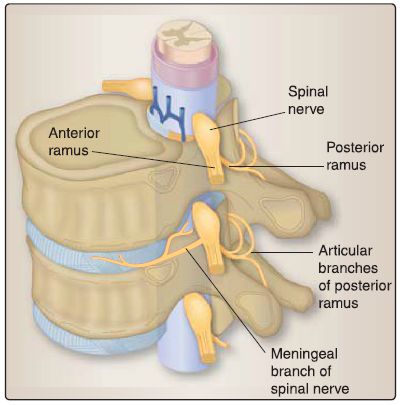
Figure 3: Neurovascular supply to the vertebral column.
 الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















