


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 18-9-2017
Date: 3-9-2017
Date: 14-8-2017
|
Hydrogenation of Benzene
The hydrogenation of benzene produces cyclohexane. Many catalyst systems, such as Ni/alumina and Ni/Pd, are used for the reaction. General reaction conditions are 160–220°C and 25–30 atmospheres. Higher temperatures and pressures may also be used with sulfided catalysts:
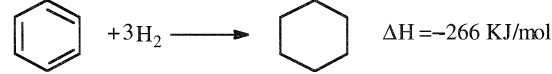
Older methods use a liquid phase process (Figure 10-11). New gasphase processes operate at higher temperatures with noble metal catalysts.
Using high temperatures accelerates the reaction (faster rate). The hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexane is characterized by a highly exothermic reaction and a significant decrease in the product volume (from 4 to 1). Equilibrium conditions are therefore strongly affected by temperature and pressure. Figure 1.1 shows the effect of H2/benzene mole ratio on the benzene content in the products. It is clear that benzene content in the product decreases with an increase of the reactor inlet pressure.
Another nonsynthetic source for cyclohexane is natural gasoline and petroleum naphtha. However, only a small amount is obtained from this source. The 1994 U.S. production of cyclohexane was approximately 2.1 billion pounds (the 45th highest chemical volume).
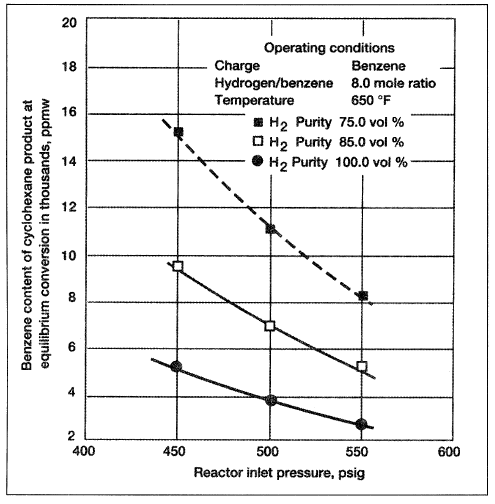
Figure 1.1. Effect of hydrogen purity and pressure on benzene conversion to cyclohexane.



|
|
|
|
مخاطر عدم علاج ارتفاع ضغط الدم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اختراق جديد في علاج سرطان البروستات العدواني
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مدرسة دار العلم.. صرح علميّ متميز في كربلاء لنشر علوم أهل البيت (عليهم السلام)
|
|
|