


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 27-7-2017
Date: 27-7-2017
Date: 7-8-2017
|
SYNTHESIS GAS
Synthesis gas generally refers to a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen. The ratio of hydrogen to carbon monoxide varies according to the type of feed, the method of production, and the end use of the gas. During World War II, the Germans obtained synthesis gas by gasifying coal. The mixture was used for producing a liquid hydrocarbon mixture in the gasoline range using Fischer-Tropsch technology. Although this route was abandoned after the war due to the high production cost of these hydrocarbons, it is currently being used in South Africa, where coal is inexpensive (SASOL, II, and III).
There are different sources for obtaining synthesis gas. It can be produced by steam reforming or partial oxidation of any hydrocarbon ranging from natural gas (methane) to heavy petroleum residues. It can also be obtained by gasifying coal to a medium Btu gas (medium Btu gas consists of variable amounts of CO, CO2, and H2 and is used principally as a fuel gas). Figure 1.1 shows the different sources of synthesis gas.
A major route for producing synthesis gas is the steam reforming of natural gas over a promoted nickel catalyst at about 800°C:
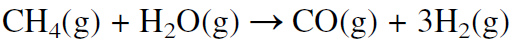
This route is used when natural gas is abundant and inexpensive, as it is in Saudi Arabia and the USA. In Europe, synthesis gas is mainly produced by steam reforming naphtha. Because naphtha is a mixture of hydrocarbons ranging approximately from C5-C10, the steam reforming reaction may be represented using n-heptane:
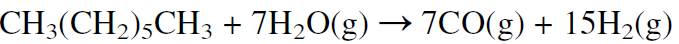
As the molecular weight of the hydrocarbon increases (lower H/C feed ratio), the H2/CO product ratio decreases. The H2/CO product ratio is approximately 3 for methane, 2.5 for ethane, 2.1 for heptane, and less than 2 for heavier hydrocarbons. Noncatalytic partial oxidation of hydrocarbons is also used to produce synthesis gas, but the H2/CO ratio is lower than from steam reforming:
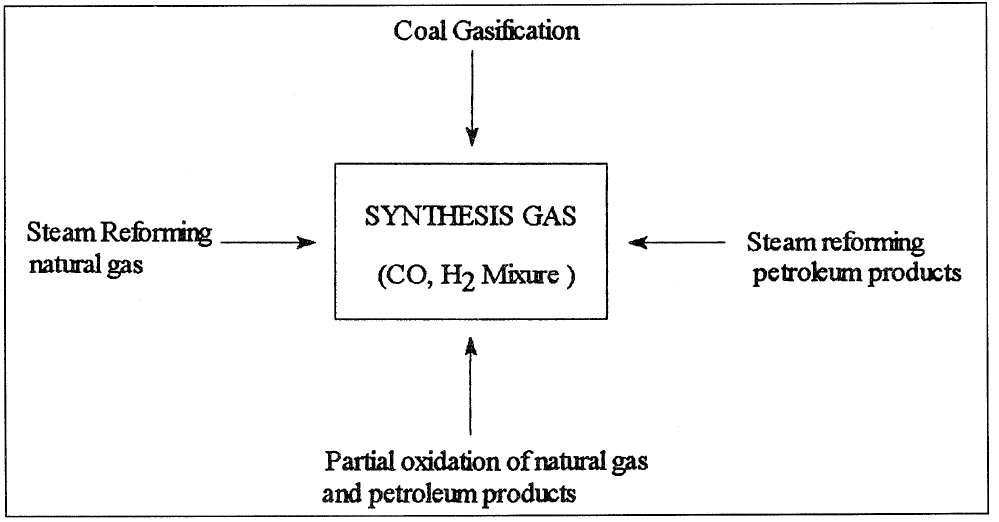
Figure 1.1. The different sources and routes to synthesis gas.
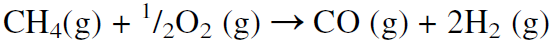
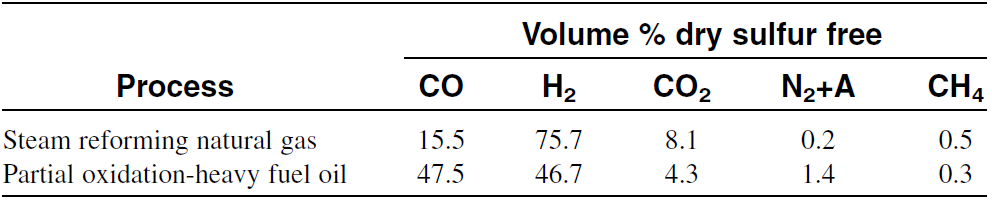
In practice, this ratio is even lower than what is shown by the stoichiometric equation because part of the methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water. When resids are partially oxidized by oxygen and steam at 1400–1450°C and 55–60 atmospheres, the gas consists of equal parts of hydrogen and carbon monoxide. Table 1.1 compares products from steam reforming natural gas with products from partial oxidation of heavy fuel oil.
Table 1.1: Composition of synthesis gas from steam reforming natural gas and partial oxidation of fuel oil



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|