


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 15-8-2017
Date: 11-8-2017
Date: 27-7-2017
|
Production of Butadiene
Butadiene is obtained as a by-product from ethylene production. It is then separated from the C4 fraction by extractive distillation using furfural. Butadiene could also be produced by the catalytic dehydrogenation of butanes or a butane/butene mixture.
CH3CH2CH2CH3 → CH2=CH-CH=CH2 + 2H2
The first step involves dehydrogenation of the butanes to a mixture of butenes which are then separated, recycled, and converted to butadiene. Figure 1.1 is the Lummus fixed-bed dehydrogenation of C4 mixture to butadiene. The process may also be used for the dehydrogenation of mixed amylenes to isoprene. In the process, the hot reactor effluent is quenched, compressed, and cooled. The product mixture is extracted: unreacted butanes are separated and recycled, and butadiene is recovered.
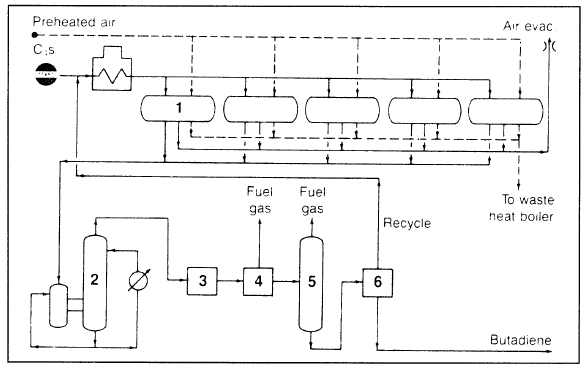
Figure 1.1. Flow diagram of the Lummus process for producing butadiene: (1) reactor, (2) quenching, (3) compressor, (4) cryogenic recovery, (5) stabilizer, (6) extraction.
The Phillips process uses an oxidative-dehydrogenation catalyst in the presence of air and steam. The C4 mixture is passed over the catalyst bed at 900 to 1100°C. Hydrogen released from dehydrogenation reacts with oxygen, thus removing it from the equilibrium mixture and shifting the reaction toward the formation of more butadiene. An in-depth study of the oxidative dehydrogenation process was made by Welch et al. They concluded that conversion and overall energy costs are favorable for butadiene production via this route.
In some parts of the world, as in Russia, fermented alcohol can serve as a cheap source for butadiene. The reaction occurs in the vapor phase under normal or reduced pressures over a zinc oxide/alumina or magnesia catalyst promoted with chromium or cobalt. Acetaldehyde has been suggested as an intermediate: two moles of acetaldehyde condense and form crotonaldehyde, which reacts with ethyl alcohol to give butadiene and acetaldehyde.
Butadiene could also be obtained by the reaction of acetylene and formaldehyde in the vapor phase over a copper acetylide catalyst. The produced 1,4-butynediol is hydrogenated to 1,4-butanediol. Dehydration of 1,4-butanediol yields butadiene.
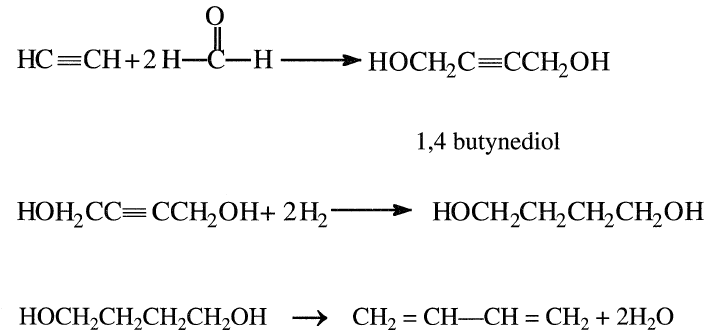



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|