


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 12-2-2017
Date: 2-2-2017
Date: 29-1-2017
|
Gravitational capture
Let us consider now the motion of a test particle in which its trajectory terminates in the black hole. Two types of such a motion are possible. First, the trajectory of the particle starts at infinity and ends in the black hole. Second, the trajectory starts and ends in the black hole. Of course, a particle cannot be ejected from the black hole. Hence, the motion on the second-type trajectory becomes possible either if the particle was placed on this trajectory via a non-geodesic curve or if the particle was created close to the black hole.
The gravitational capture of a particle coming from infinity is of special interest. Let us have a better look at this case. It is clear from the analysis of motion given in the preceding section that a particle coming from infinity can be captured if its specific energy Ẽ is greater, for a given ˜L, than the maximum (Ẽmax) of the curve V (r ). Let us consider the gravitational capture in two limiting cases, one for a particle whose velocity at infinity is much lower than the speed of light (v∞/c << 1) and another for a particle which is ultrarelativistic at infinity.
In the former case, Ẽ ≈ 1. The curve V (r ), which has Ẽmax = 1, corresponds to ˜Lcr = 2 (line c in figure 5.2). The maximum of this curve lies at r = 2rS. This radius is minimal for the periastra of the orbits of the particles with v∞ = 0 which approach the black hole and again recede to infinity. If ˜L ≤ 2, gravitational capture takes place. The angular momentum of a particle moving with the velocity v∞ at infinity is L = mv∞b, where b is the impact parameter. The condition ˜L ≡ L/mcrS = 2 defines the critical value bcr,nonrel = 2rS (c/v∞) of the impact parameter for which the capture takes place. The capture cross section for a non-relativistic particle is
 (1.1)
(1.1)
For an ultrarelativistic particle, bcr = 3√3rS/2, and the capture cross section is
 (1.2)
(1.2)
Owing to a possible gravitational capture, not every particle whose velocity exceeds the escape limit flies away to infinity. In addition, it is necessary that the angle ψ between the direction to the black hole center and the trajectory be greater than a certain critical value ψcr. For the velocity equal to the escape threshold this critical angle is given by the expression
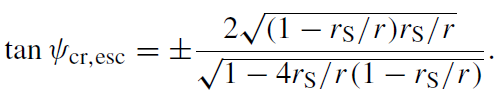 (1.3)
(1.3)
The plus sign is chosen for r > 2rS (ψcr < 90o), and the minus sign for r < 2rS (ψcr > 90o).
For an ultrarelativistic particle, the critical angle is given by the formula
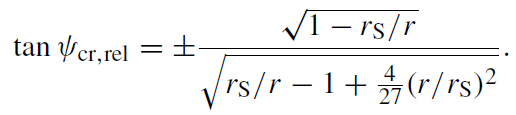 (1.4)
(1.4)
The plus sign is taken for r > 1.5rS and the minus for r < 1.5rS.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|