


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 2-7-2017
Date: 22-6-2021
Date: 14-7-2021
|
Definition : Let X and Y be topological spaces and let q: X → Y be a function from X to Y . The function q is said to be an identification map if
and only if the following conditions are satisfied:
• the function q: X → Y is surjective,
• a subset U of Y is open in Y if and only if q−1 (U) is open in X.
It follows directly from the definition that any identication map is continuous. Moreover, in order to show that a continuous surjection q: X → Y is an identification map, it suffices to prove that if V is a subset of Y with the property that q−1 (V ) is open in X then V is open in Y .
Lemma 1.1 Let X be a topological space, let Y be a set, and let q: X → Y be a surjection. Then there is a unique topology on Y for which the function q: X → Y is an identification map.
Proof Let τ be the collection consisting of all subsets U of Y for whichq−1 (U) is open in X. Now q−1 (∅) = ∅, and q−1 (Y ) = X, so that ∅ ∈ τ andY ∈ τ . If {Vα : α ∈ A} is any collection of subsets of Y indexed by a set A, then it is a straightforward exercise to verify that
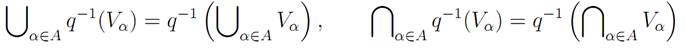
(i.e., given any collection of subsets of Y , the union of the preimages of the sets is the preimage of the union of those sets, and the intersection of the preimages of the sets is the preimage of the intersection of those sets). It follows easily from this that unions and finite intersections of sets belonging to τ must themselves belong to τ . Thus τ is a topology on Y , and the function q: X → Y is an identification map with respect to the topology τ . Clearly τ is the unique topology on Y for which the function q: X → Y is an identification map
Let X be a topological space, let Y be a set, and let q: X → Y be a surjection. The unique topology on Y for which the function q is an identification map is referred to as the quotient topology (or identification topology) on Y .
Lemma 1.2 Let X and Y be topological spaces and let q: X → Y be an identification map. Let Z be a topological space, and let f: Y → Z be a function from Y to Z. Then the function f is continuous if and only if the composition function f ◦ q: X → Z is continuous
Proof Suppose that f is continuous. Then the composition function f ◦ q is a composition of continuous functions and hence is itself continuous.
Conversely suppose that f ◦ q is continuous. Let U be an open set in Z.
Then q−1 (f−1 (U)) is open in X (since f ◦ q is continuous), and hence f−1 (U) is open in Y (since the function q is an identification map). Therefore the function f is continuous, as required.
Example Let S1 be the unit circle in R2, and let q: [0, 1] → S1 be the map that sends t ∈ [0, 1] to (cos 2πt,sin 2πt). Then q: [0, 1] → S1is an identification map, and therefore a function f: S1 → Z from S1to some topological space Z is continuous if and only if f ◦q: [0, 1] → Z is continuous.
Example :Let Sn be the n-sphere, consisting of all points x in Rn+1 satisfying |x| = 1. Let RPn be the set of all lines in Rn+1 passing through the origin (i.e., RPnis the set of all one dimensional vector subspaces of Rn+1). Let q: Sn → RPn denote the function which sends a point x of Sn to the element of RPnrepresented by the line in Rn+1 that passes through both x and the origin. Note that each element of RPn is the image (under q) of exactly two antipodal points x and x of Sn. The function q induces a corresponding quotient topology on RPn such that q: Sn → RPn is an identification map. The set RPn, with this topology, is referred to as real projective n-space. In particular RP2 is referred to as the real projective plane. It follows from Lemma 1.10 that a function f: RPn → Z from RPn to any topological space Z is continuous if and only if the composition function f ◦ q: S n → Z is continuous.



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ضمن أسبوع الإرشاد النفسي.. جامعة العميد تُقيم أنشطةً ثقافية وتطويرية لطلبتها
|
|
|