


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 21-8-2016
Date: 26-8-2016
Date: 3-9-2016
|
Two-Dimensional Debye Solid
An atom confined to a surface may be thought of as an object “living” in a two-dimensional world. There are a variety of ways to look at such an atom. Suppose that the atoms adsorbed on the surface are not independent but undergo collective oscillations as do the atoms in a Debye crystal. Unlike the atoms in a Debye crystal, however, there are only two dimensions in which these collective vibrations can occur.
a) Derive an expression for the number of normal modes between ω and ω + dω and, by thinking carefully about the total number of vibrational frequencies for N atoms confined to a surface, rewrite it in terms of N and ωD, the maximum vibration frequency allowed due to the discreteness of the atoms.
b) Obtain an integral expression for the energy E for the two- dimensional Debye crystal. Use this to determine the limiting form of the temperature dependence of the heat capacity (analogous to the Debye τ3 law) as τ → 0 for the two-dimensional Debye crystal up to dimensionless integrals.
SOLUTION
a) The number of normal modes in the 2D solid within the interval dk of a wave vector k may be written
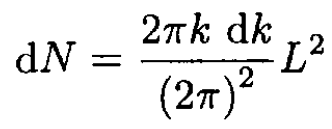 (1)
(1)
In the 2D solid there are only two independent polarizations of the excitations, one longitudinal and one transverse. Therefore,
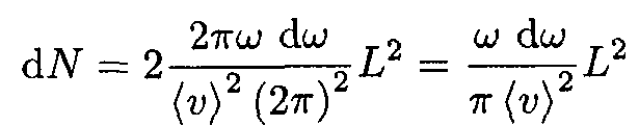 (2)
(2)
where ⟨v⟩ is the average velocity of sound. To find the Debye frequency ωD, we use the standard assumption that the integral of (2) from 0 to a certain cut-off frequency ωD is equal to the total number of vibrational modes; i.e.,
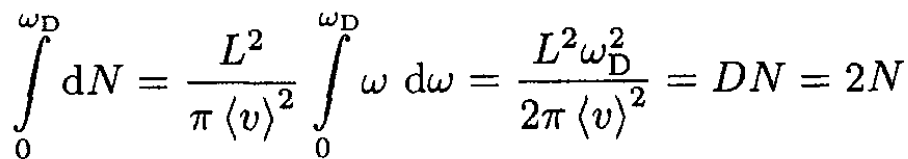 (3)
(3)
Therefore,
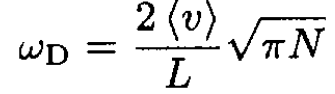 (4)
(4)
We can express ⟨v⟩ through ωD:
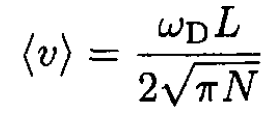 (5)
(5)
Then (2) becomes
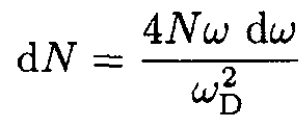 (6)
(6)
b) The free energy then becomes
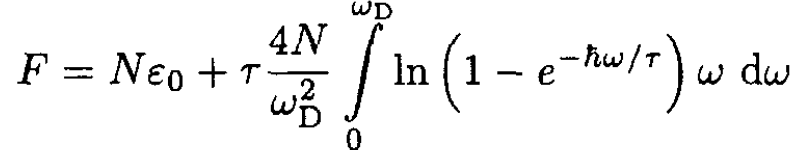 (6)
(6)
Defining θD = hωD, and introducing a new variable x = hω/τ, we can rewrite (7) in the form
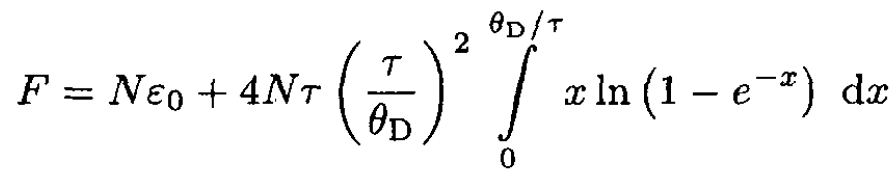 (8)
(8)
Integrating (8) by parts, we obtain
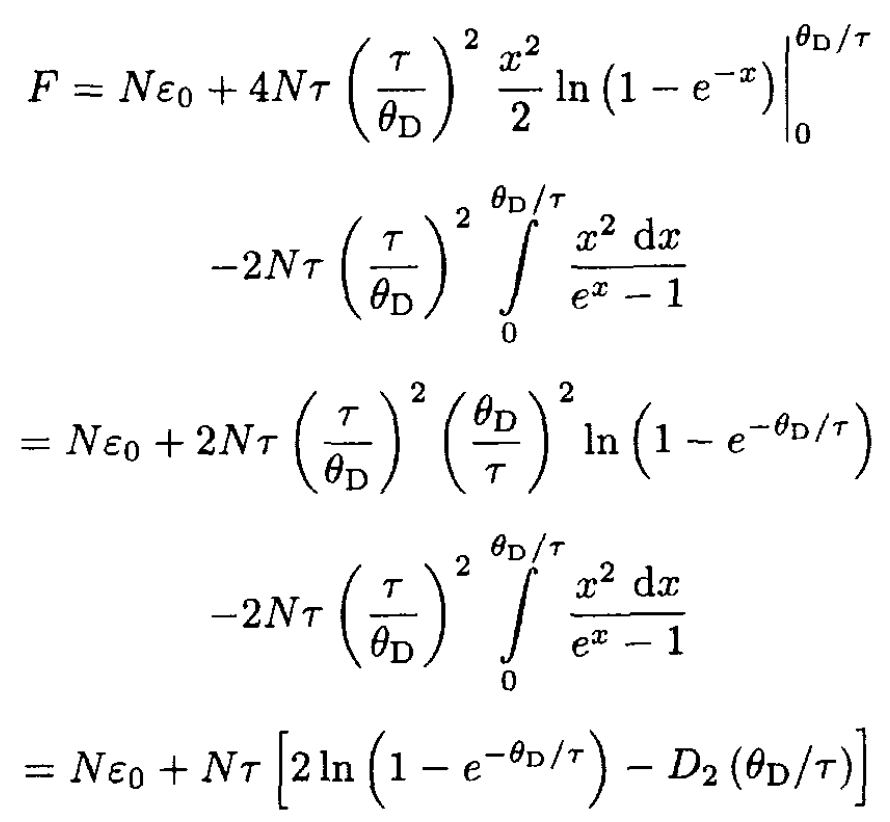 (9)
(9)
where the 2D Debye function D2(z) is
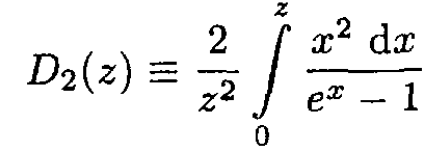 (10)
(10)
The energy is given by
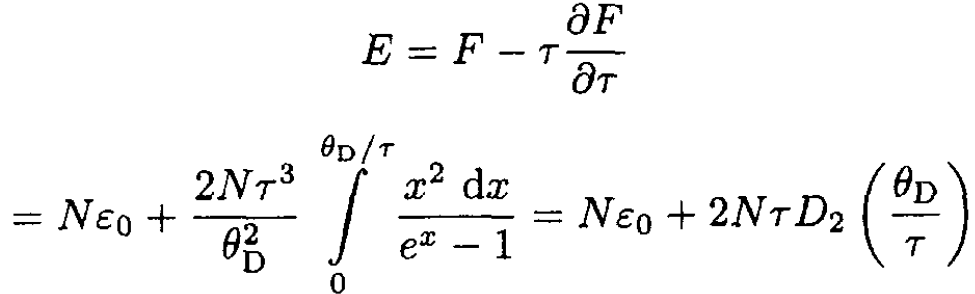 (11)
(11)
The specific heat C (CP ≈ CV at low temperatures) is
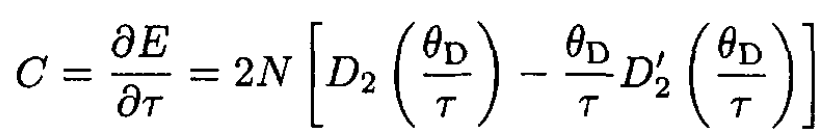 (12)
(12)
At low temperatures, τ << θD, we can extend the upper limit of integration to infinity:
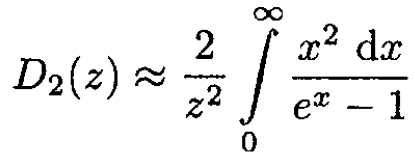
Therefore, at τ << θD,
 (13)
(13)
where

and 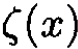 is the Riemann
is the Riemann 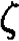 function. Note that the specific heat in 2D is
function. Note that the specific heat in 2D is

Note also that you can solve a somewhat different problem: When atoms are confined to the surface but still have three degrees of freedom, the results will, of course, be different.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
وفد كلية الزراعة في جامعة كربلاء يشيد بمشروع الحزام الأخضر
|
|
|