


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية | Cells Are the Structural and Functional Units of All Living Organisms |
|
|
|
Read More
Date: 12-4-2017
Date: 25-7-2016
Date: 15-4-2017
|
Cells Are the Structural and Functional Units of All Living Organisms
Cells of all kinds share certain structural features (Fig. 1–1). The plasma membrane defines the periphery of the cell, separating its contents from the surroundings. It is composed of lipid and protein molecules that form a thin, tough, pliable, hydrophobic barrier around the cell. The membrane is a barrier to the free passage of inorganic ions and most other charged or polar compounds. Transport proteins in the plasma membrane allow the passage of certain ions and molecules; receptor proteins transmit signals into the cell; and membrane enzymes participate in some reaction pathways. Because the individual lipids and proteins of the plasma membrane are not covalently linked, the entire structure is remarkably flexible, allowing changes in the shape and size of the cell. As a cell grows, newly made lipid and protein molecules are inserted into its plasma membrane; cell division produces two cells, each with its own membrane. This growth and cell division (fission) occurs without loss of membrane integrity.
The internal volume bounded by the plasma membrane, the cytoplasm (Fig. 1–1), is composed of an aqueous solution, the cytosol, and a variety of suspended particles with specific functions.
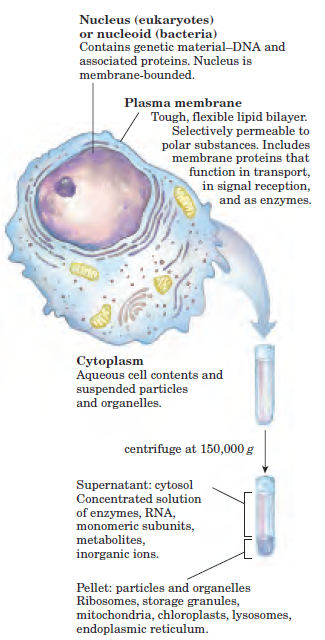
FIGURE 1–1 The universal features of living cells. All cells have a nucleus or nucleoid, a plasma membrane, and cytoplasm. The cytosol is defined as that portion of the cytoplasm that remains in the supernatant after centrifugation of a cell extract at 150,000 g for 1 hour.
The cytosol is a highly concentrated solution containing enzymes and the RNA molecules that encode them; the components (amino acids and nucleotides) from which these macromolecules are assembled; hundreds of small organic molecules called metabolites, intermediates in biosynthetic and derivative pathways; coenzymes, compounds essential to many enzyme-catalyzed reactions; inorganic ions; and ribosomes, small particles (composed of protein and RNA molecules) that are the sites of protein synthesis. All cells have, for at least some part of their life, either a nucleus or a nucleoid, in which the genome— the complete set of genes, composed of DNA—is stored and replicated. The nucleoid, in bacteria, is not separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane; the nucleus, in higher organisms, consists of nuclear material enclosed within a double membrane, the nuclear envelope. Cells with nuclear envelopes are called eukaryotes (Greek eu, “true,” and karyon, “nucleus”); those without nuclear envelopes—bacterial cells—are prokaryotes (Greek pro, “before”).



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|