


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 13-2-2016
Date: 9-5-2016
Date: 31-8-2017
|
Thermal Cracking Reactions
The first step in cracking is the thermal decomposition of hydrocarbon molecules to two free radical fragments. This initiation step can occur by a homolytic carbon-carbon bond scission at any position along the hydrocarbon chain. The following represents the initiation reaction:
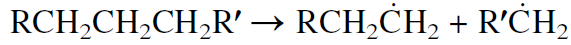
The radicals may further crack, yielding an olefin and a new free radical. Cracking usually occurs at a bond beta to the carbon carrying the unpaired electron.
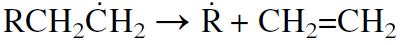
Further β bond scission of the new free radical R˙ can continue to produce ethylene until the radical is terminated.
Free radicals may also react with a hydrocarbon molecule from the feed by abstracting a hydrogen atom. In this case the attacking radical is terminated, and a new free radical is formed. Abstraction of a hydrogen atom can occur at any position along the chain. However, the rate of hydrogen abstraction is faster from a tertiary position than from a secondary, which is faster than from a primary position.
The secondary free radical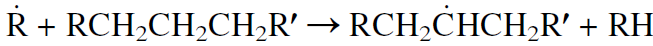 can crack on either side of the carbon carrying the unpaired electron according to the beta scission rule, and a terminal olefin is produced.
can crack on either side of the carbon carrying the unpaired electron according to the beta scission rule, and a terminal olefin is produced.
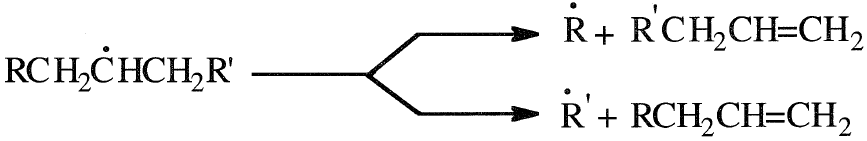
Free radicals, unlike carbocations, do not normally undergo isomerization by methyl or hydrogen migration. However, hydrogen transfer (chain transfer) occurs when a free radical reacts with other hydrocarbons. There are two major commercial thermal cracking processes, delayed coking and fluid coking. Flexicoking is a fluid coking process in which the coke is gasified with air and steam. The resulting gas mixture partially provides process heat.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|