


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 18-4-2016
Date: 18-4-2016
Date: 19-4-2016
|
Introduction to Immunological methods
Antibodies are proteins made by the immune system of animals as part of a defense system against infection by foreign organisms. The immune system must be able to distinguish between “self” and “non-self”, and to eliminate the latter, and antibodies play a role in this process. Because of their specificity and versatility, antibodies are also very useful reagents in the identification and analysis of proteins and it is largely in this light - as useful reagents.
The structure of antibodies
Antibodies are a class of blood proteins known as γ-globulin . The most common γ-globulin is the IgG type, which consists of four peptide chains, two heavy and two light, held together by disulfide bonds. A schematic sketch of the structure is shown in Fig. 1.
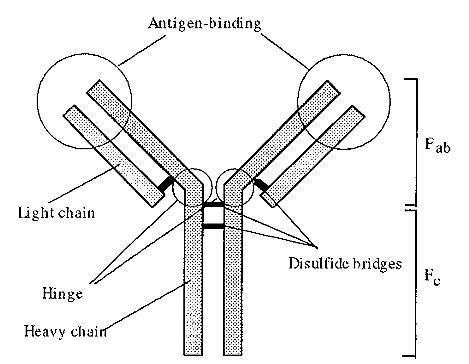
Figure 1. A simplified schematic representation of the structure of an IgG antibody.
The IgG molecule can be cleaved in the hinge region by papain, to yield three fragments, two Fab fragments and one Fc fragment. “F ab” stands for “fragment, antigen binding” and this reflects the fact that the outer aspect of the heavy and light chains, in the Fab fragment, contain so-called hypervariable regions which constitute the antigen binding site.
The hypervariable regions are different in the IgG molecules synthesized by different plasma cell clones, but will be identical in every molecule originating from a single clone of plasma cells. The hypervariable regions are constituted of loops at one end of a fl-barrel structure, Such loops can vary without disturbing the underlying stability of the barrel structure. “F c” stands for “fragment, crystallizable” and this reflects the fact that the Fc fragment is invariant and therefore can be crystallized, even when it is derived from a polyclonal antiserum. In mammals, antibodies are transferred to the neonate in the form of colostrum, which is the first milk produced in the early post-partum stage. In birds the transfer of antibodies occurs via the egg yolk and egg yolk thus provides a convenient source from which antibodies may be isolated. The antibodies from egg yolk have a structure similar, but not identical, to IgG and are known as IgY antibodies.
References
Dennison, C. (2002). A guide to protein isolation . School of Molecular mid Cellular Biosciences, University of Natal . Kluwer Academic Publishers new york, Boston, Dordrecht, London, Moscow .



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
هيأة المساءلة والعدالة: مؤتمر ذاكرة الألم يوثّق سنوات القهر التي عاشها العراقيون إبّان الحكم الجائر
|
|
|