


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 25-12-2020
Date: 22-2-2016
Date: 24-12-2020
|
Poliomyelitis
Causative agent poliovirus is the member of the family picornaviridae which is one of the largest and most important families of human pathogens .these are smallest RNA viruses .Despite a member of enterovirus poliovirus as well as other enterovirus don’t produce enteric disease they are named because the alimentary canal is their predominant site of replication
Vaccine against poliomyelitis
There are two kinds of vaccines for immunization against virus
Oral polio virus vaccine
the trivalent oral poliovirus vaccine TOPV is mixture of three types (monovalent ) of attenuated polioviruses which are propagated separately in appropriate cell cultures and then mixed .A stabilizer magnesium chloride is added to this blended mixture .Each dose contains less than 25μg of each of the antibiotics ,streptomycin and neomycin .phenol added as indicator of the PH, before being released by the manufacturer the vaccine in final containers is kept continuously in the frozen temperature below -20 C .under this condition of storage ,the expiry date of vaccine is fixed which is not more than two years. after thawing OPV may be refrigerated at temperature of 2-8 C for a period not exceeding 30 days .
inactivated poliovirus vaccine
this vaccine contains 40,8 and 32 D unit respectively of type 1,2 and 3 in each dose of the vaccine which gives adequate immunity after two doses given parenterally
Advantages with IPV
Disadvantage of IPV
Advantage with OPV
Disadvantage with OPV
Differences between OPV and IPV
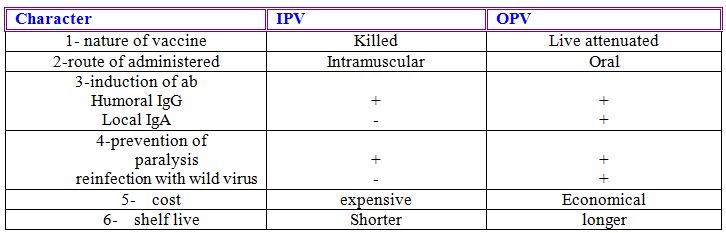
Efficacy of poliovirus vaccine
The presence of humoral antibodies has been seen after 7-15 years of immunization with IPV
IPV has also been shown to induce good protection in persons in tropical countries where OPV may fail to uniformly immunize because of the presence of the inhibitors of the vaccine virus in the gastrointestinal tract especially in developing tropical countries .
OPV : the persistence of humoral ab after vaccinating with OPV has been reported up to 15 years or even more . Seroconversion in virtually 100% recipients .There are several problems with OPV such as occurrence of vaccine associated paralytic poliomyelitis cases in developed countries and failure of OPV to cause seroconversion .
OPV is unstable unless kept at very low temperature .Current recommendations indicate that after thawing ,OPV be held at no more than 10 C for less than 30 days .At 0-8 C the virus can be stored for 6-12 months without a loss in titre.
Immunization schedules
OPV : the centres for disease control (CDC) recommends that primary immunization with OPV should commence at the age of two months ,the second and third doses should be given at 2 months interval there after ,and fourth dose should be given at 18 months of age .
If the child vomits within one hour of receiving the oral poliovaccine a further dose may be given the next day .
Contraindication to OPV
1-Acute febrile illness b- sever diarrhea and vomiting c- Sensitivity to antimicrobial agents in vaccine preparation
d- Immunodeficiency and malignancy e- pregnancy f- If there has been a serious reaction t o a previous vaccination with OPV eg .anaphylactic reaction
Adverse reactions
Vaccine associated paralysis in recipients is very rare about one in 2 million doses administration
IPV : The CDC recommends first dose of IPV at 6-12 weeks of age followed by two doses after intervals of 4-8 weeks .The fourth dose is recommended after 6-12 months of the third dose and supplementary booster at the age of 4-6 years ,Subsequent boosters may be administered every five years till the age of 18 years .



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي للقرآن الكريم يقيم جلسة حوارية لطلبة جامعة الكوفة
|
|
|