


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 14-9-2017
Date: 25-7-2017
Date: 23-8-2017
|
Alkanes (Paraffins)
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons having the general formula CnH2n+2. The simplest alkane, methane (CH4), is the principal constituent of natural gas. Methane, ethane, propane, and butane are gaseous hydrocarbons at ambient temperatures and atmospheric pressure. They are usually found associated with crude oils in a dissolved state. Normal alkanes (n-alkanes, n-paraffins) are straight-chain hydrocarbons having no branches. Branched alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with an alkyl substituent or a side branch from the main chain. Abranched alkane with the same number of carbons and hydrogens as an n-alkane is called an isomer. For example, butane (C4H10) has two isomers, n-butane and 2-methyl propane (isobutane). As the molecular weight of the hydrocarbon increases, the number of isomers also increases. Pentane (C5C12) has three isomers; hexane (C6H14) has five. The following shows the An isoparaffin is an isomer having a methyl group branching from carbon number 2 of the main chain.
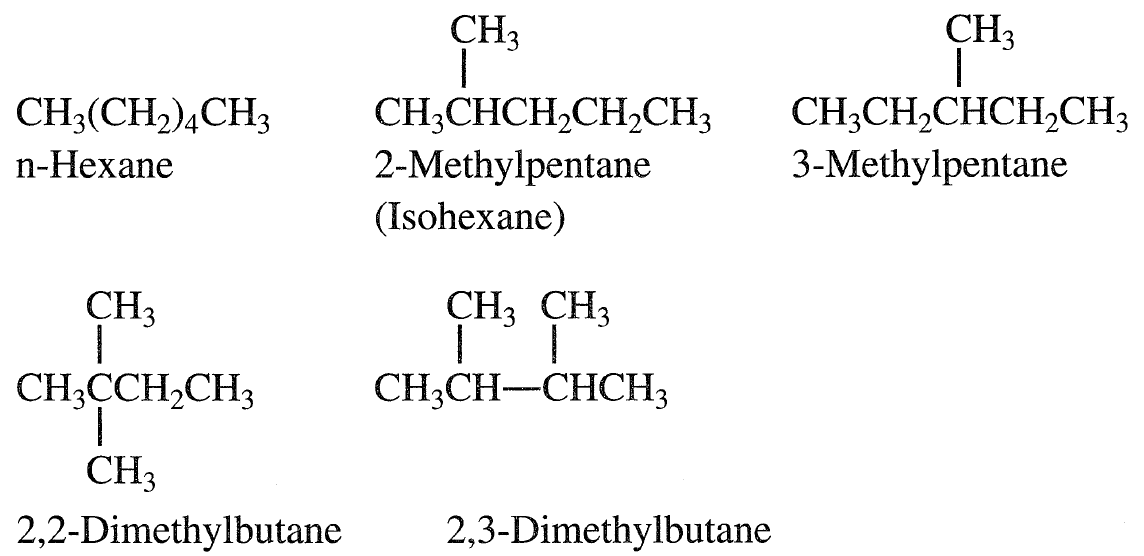
A naphtha fraction (obtained as a light liquid stream from crude fractionation) with a narrow boiling range may contain a limited but still large number of isomers.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
بالصور: تزامنا مع ختام فعالياته.. ممثل المرجعية العليا يشارك في المحفل القرآني المركزي في الصحن الحسيني الشريف
|
|
|