


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 4-11-2015
Date: 4-11-2015
Date: 4-11-2015
|
Plasma Membrane
It is the outer limiting membrane of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It is an ultra-thin, elastic, living membrane. Plasma membrane is a dynamic and selective transport barrier.
Since the plasma membrane is ultra-thin, it could be observed only under electron microscope. Structure of the membrane is studied by isolating the same from the cell and conducting biochemical investigations.
In 1895 Overton suggested that the membrane is made of fatty sub-stances. Other workers later concluded that two layers of lipid were present in the cell membrane.
According to a model proposed by Danielli and Davson in 1935, the lipid bilayer of the membrane was coated on either side with protein.
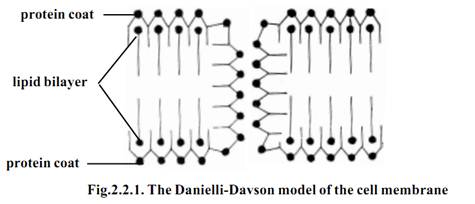
In 1960, Robertson using electronmicrographs proposed a unit membrane hypothesis. According to this hypothesis the two outer layers of protein are about 2 nm thick and appear densely granular. They enclose a clear central area of about 3.5 nm wide consisting of lipids. The lipids are mainly phospholipid molecules.
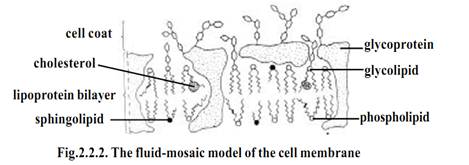
Singer and Nicholson (1972) have proposed a fluid mosaic model for the plasma membrane. The fluid mosaic membrane is a dynamic structure. In this structure much of the protein molecules float about. Some of them are anchored to the organelles within the cell. Lipid molecules also move about. ‘Fluid mosaic model’ is applied to all biological membranes in general.
The cell membrane controls the passage of materials both into and out of the cell. It regulates the passage of water and dissolved substances. Water passes through the membrane by Osmosis. Water soluble substances cross the membrane by diffusion or by active transport. Many water soluble solutes are transported by carrier proteins. Lipid soluble compounds pass more quickly by dissolving in the phospholipid layer.
References
T. Sargunam Stephen, Biology (Zoology). First Edition – 2005, Government of Tamilnadu.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|