


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2024-12-17
Date: 2024-02-21
Date: 2025-02-21
|
/r/
Scottish Standard English is generally rhotic (Wells 1982: 10–11); in the 1997 Glasgow data articulated /r/ made up around 90% of all variants for postvocalic /r/ in middle-class speakers (Stuart-Smith 2003: 128–129.). In Urban Scots /r/- vocalization is becoming increasingly common (Johnston 1997: 511). Romaine (1978) reported loss of postvocalic /r/ in the speech of working-class children in Edinburgh, where she also noted gendered distribution of variants, with girls showing more approximants and boys showing more r-lessness. The analysis of postvocalic /r/ in the Glasgow data confirmed Macafee’s (1983: 32) comments in the discovery of extensive /r/-vocalization in working-class adolescents (Stuart-Smith 2003). Two ‘vowel’ variant categories were set up: vowels with audible secondary velarization/pharyngealization (cf. Johnston 1997: 511), and ‘plain’ vowels with no audible secondary articulation. Interestingly, there appears to be subtle conditioning according to gender in the use of these variants: girls overall tended to vocalize more, and to favor plain vowels, especially in contexts such as before a consonant, e.g. card or unstressed prepausal, e.g. better; boys used both plain and velarized variants before a consonant, but preferred velarized vowels in words like better (Stuart-Smith 2003: 126–135).
The phonetic realization of /r/ is variable. Wells states that trills are unusual, and certainly I have rarely heard them amongst Scottish English students. More usual are approximants, post-alveolar 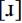 and retroflex
and retroflex  , and alveolar taps
, and alveolar taps 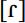 , which vary according to position in the word, phonetic environment, and sociolinguistic factors. Scots is usually said to favor taps, though Johnston (1997: 510) notes that
, which vary according to position in the word, phonetic environment, and sociolinguistic factors. Scots is usually said to favor taps, though Johnston (1997: 510) notes that 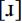 , more typical of Scottish Standard English, is encroaching. My analysis of the realization of /r/ in the Glasgow data showed that all variants were present in all speakers, with differences in distributional patterns and tendencies. Taps emerged as more common in working-class speakers (especially men) but only in read speech; retroflex approximants were more common in middle-class speakers. There was a slight tendency for the working-class adolescents, who produced a high proportion of vocalized variants, to use taps for articulated /r/.
, more typical of Scottish Standard English, is encroaching. My analysis of the realization of /r/ in the Glasgow data showed that all variants were present in all speakers, with differences in distributional patterns and tendencies. Taps emerged as more common in working-class speakers (especially men) but only in read speech; retroflex approximants were more common in middle-class speakers. There was a slight tendency for the working-class adolescents, who produced a high proportion of vocalized variants, to use taps for articulated /r/.
|
|
|
|
4 أسباب تجعلك تضيف الزنجبيل إلى طعامك.. تعرف عليها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أكبر محطة للطاقة الكهرومائية في بريطانيا تستعد للانطلاق
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مكتوبة بالخط الكوفي قسم الشؤون الفكرية يشرع بترميم صفحات من مصحف نادر يعود للقرن الرابع الهجري
|
|
|