

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Hydrogenation with Homogeneous Catalysts
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
الجزء والصفحة:
........
21-1-2022
3667
Hydrogenation with Homogeneous Catalysts
Hydrogen addition to multiple bonds is catalyzed by certain complex metal salts in solution. This may be described as homogeneous catalysis and, compared to heterogeneous catalysis, is a relatively new development in the area of hydrogenation reactions. Rhodium and ruthenium salts appear to be generally useful catalysts:
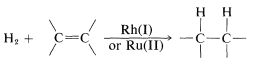
At present, homogeneous catalysis for routine hydrogenation reactions offers little advantage over the convenience and simplicity of heterogeneous catalysis. Suprafacial addition of hydrogen is observed with both types of catalytic systems. However, greater selectivity can be achieved with homogeneous catalysts because they appear to be more sensitive to steric hindrance and are less likely to cause rearrangement, dissociation, and hydrogenation of other bonds (e.g., −NO2 and 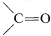 ).
).
The most thoroughly investigated homogeneous hydrogenation catalyst is the four-coordinated rhodium complex Rh[(C6H5)3P]3Cl. This catalyst is called Wilkinson's catalyst after its discoverer, G. Wilkinson. In 1973, the Nobel Prize in chemistry was awarded jointly to Wilkinson and E. O. H. Fischer for their respective contributions to the field of organometallic chemistry. As you will see in this and later chapters, compounds with carbon-metal bonds (organometallic compounds) are extremely useful reagents, reactive intermediates, or catalysts in organic reactions.
 الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















