

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
الجزء والصفحة:
........
19-1-2022
7698
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
When a stepwise ionic addition reaction involves nucleophilic attack at carbon as a first step, it is described as a nucleophilic addition. Reactions of this type often are catalyzed by bases, which generate the required nucleophile. For example, consider the addition of some weakly acidic reagent HX to an alkene. In the presence of a strong base (⊖OH), HX could give up its proton to form the conjugate base X⊖, which is expected to be a much better nucleophile than HX:
H:X+⊖OH⇌H2O+:X⊖ (10.7.1)
What can follow with an alkene is an ionic chain reaction with the following two propagating steps. First, the nucleophile attacks at carbon to form a carbon anion (carbanion) intermediate (Equation 10-8). Second, electrophilic transfer of a proton from HX to the carbanion forms the adduct and regenerates the nucleophile (Equation 10-9). The overall reaction is the addition of HX to the double bond:
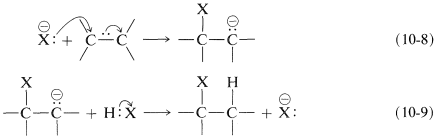
Net reaction: 
The HX reagent can be water, an alcohol (ROH), a thiol (RSH), an amine (RNH2), or hydrogen cyanide (HCN) or other carbon acids (i.e., compounds with acidic C−H bonds). However, nucleophilic addition of these reagents to simple alkenes rarely is encountered. To have nucleophilic addition the double bond must be substituted with strongly electron-withdrawing groups such as carbonyl-containing groups, NO2, C≡N, or positively charged ammonium or sulfonium groups. However, alkynes generally are more reactive towards nucleophiles than they are toward electrophiles. For example, with a base catalyst, 2-hexen-4-yne adds methanol across the triple bond, leaving the double bond untouched:
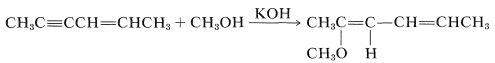
(Nonetheless, the double bond seems to be necessary because a corresponding addition is not observed for 2-butyne, CH3C≡CCH3.)
Many nucleophilic addition reactions have considerable synthetic value, particularly those involving addition of carbon acids, such as HCN, because they provide ways of forming carbon-carbon bonds.
 الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















