


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 27-12-2021
Date: 28-12-2021
Date: 16-12-2021
|
Purine and pyrimidine bases
Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base; a pentose monosaccharide; and one, two, or three phosphate groups. The nitrogen-containing bases belong to two families of compounds: the purines and the pyrimidines.
Purine and pyrimidine bases
Both DNA and RNA contain the same purine bases: adenine (A) and guanine (G). Both DNA and RNA contain the pyrimidine cytosine (C), but they differ in their second pyrimidine base: DNA contains thymine (T), whereas RNA contains uracil (U). T and U differ in that only T has a methyl group (Fig.1). Unusual (modified) bases are occasionally found in some species of DNA (for example, in some viral DNA) and RNA (for example, in transfer RNA [tRNA]). Base modifications include methylation, glycosylation, acetylation, and reduction. Some examples of unusual bases are shown in Figure 2. [Note: The presence of an unusual base in a nucleotide sequence may aid in its recognition by specific enzymes or protect it from being degraded by nucleases.]
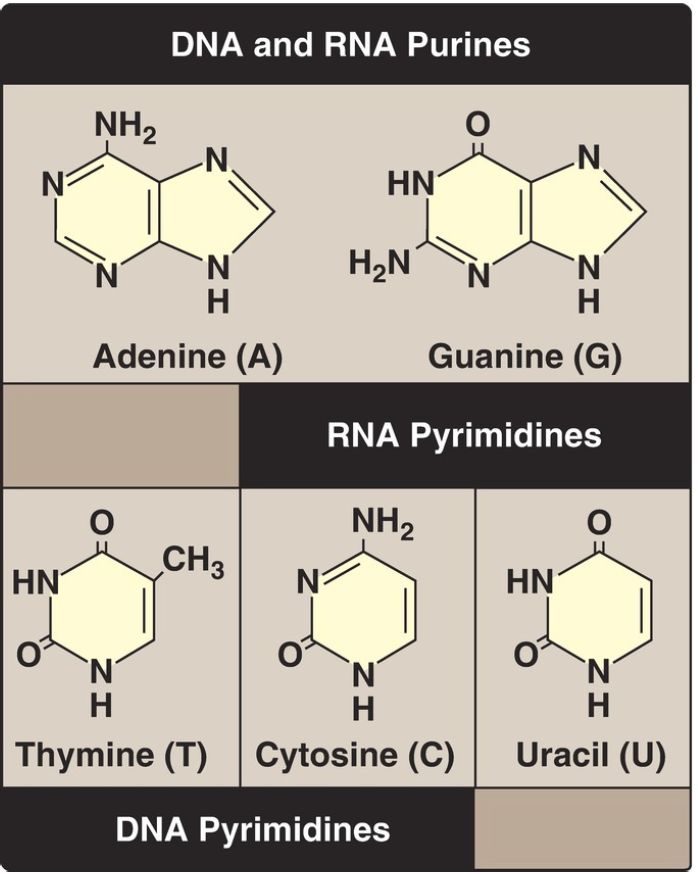
Figure .1 : Purines and pyrimidines commonly found in DNA and RNA.
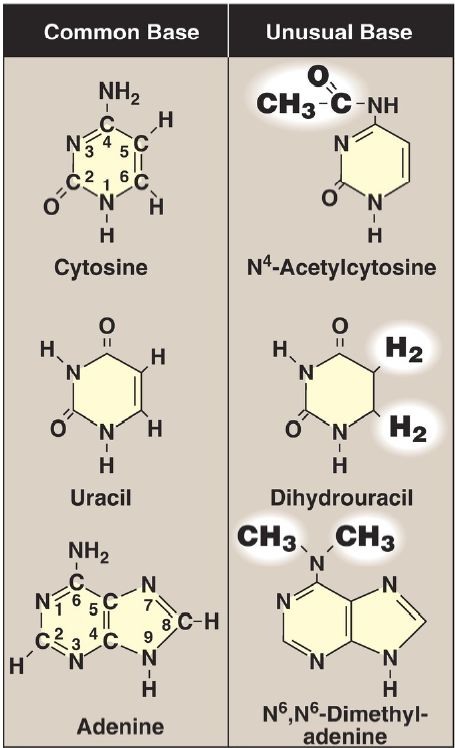
Figure.2 : Examples of unusual bases.



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ندوات وأنشطة قرآنية مختلفة يقيمها المجمَع العلمي في محافظتي النجف وكربلاء
|
|
|